Summary of Contents for T40B
Page 1: ...Mounting Instructions Montageanleitung English Deutsch T40B ...
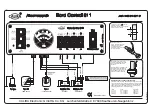
Page 3: ...Mounting Instructions Montageanleitung English Deutsch T40B ...
Page 70: ...Supplementary technical information 68 A03452_15_X00_00 HBM public T40B ...
Page 71: ...Mounting Instructions Montageanleitung English Deutsch T40B ...
Page 163: ...Dimensions Abmessungen T40B A03452_15_X00_00 HBM public 93 ...