Chapter 9 Quality of Service (QoS)
VMG1312-T10C User’s Guide
120
CoS technologies includes DiffServ (Differentiated Services or DS). DiffServ is a new protocol and
defines a new DS field, which replaces the eight-bit ToS (Type of Service) field in the IP header.
Tagging and Marking
In a QoS class, you can configure whether to add or change the DSCP (DiffServ Code Point) value
ain a matched packet. When the packet passes through a compatible network, the networking
device, such as a backbone switch, can provide specific treatment or service based on the tag or
marker.
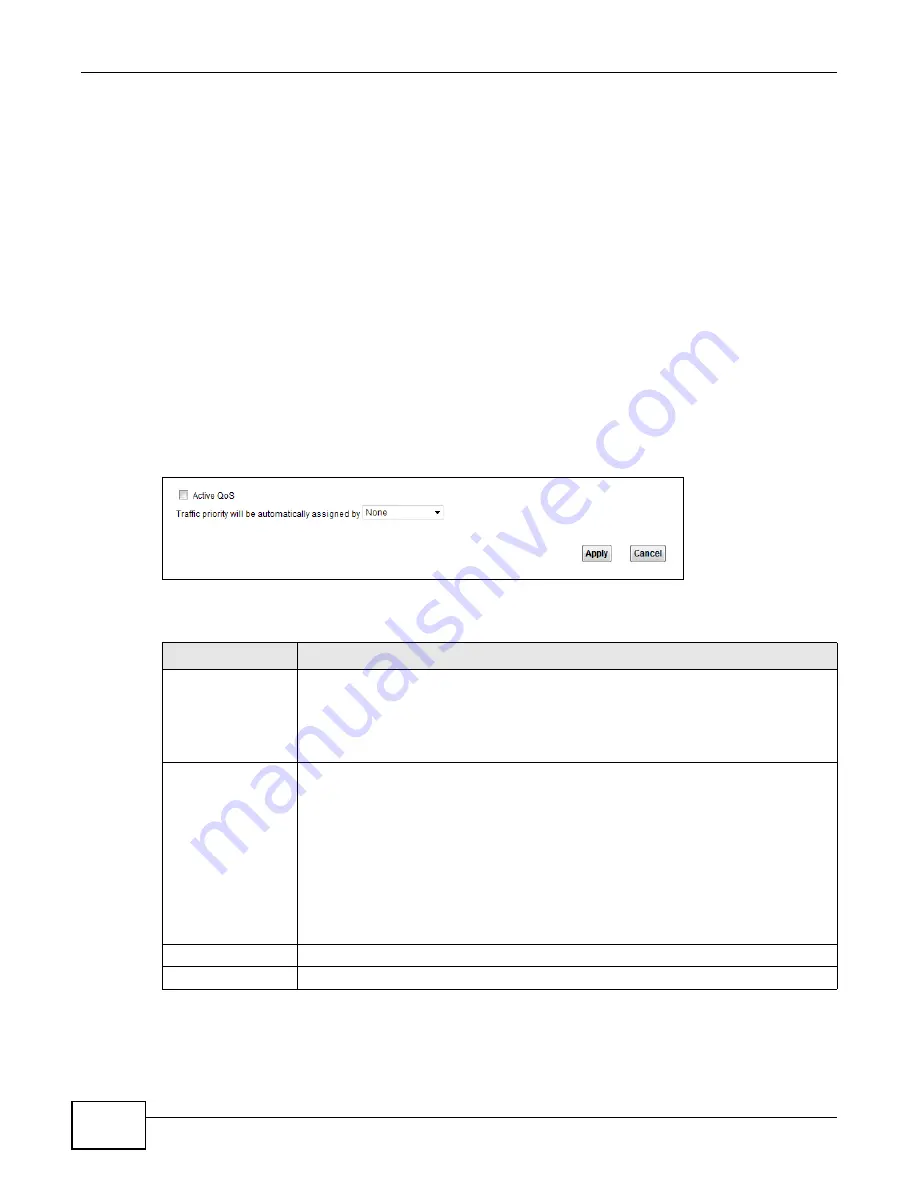
9.2 The QoS General Screen
Use this screen to enable or disable QoS, set the bandwidth, and select to have the Device
automatically assign priority to upstream traffic according to the IP precedence or packet length.
Click
Network Setting > QoS
to open the
General
screen.
Figure 79
Network Setting > QoS > General
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 39
Network Setting > QoS > General
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Active QoS
Select the check box to turn on QoS to improve your network performance.
You can give priority to traffic that the Device forwards out through the WAN interface.
Give high priority to voice and video to make them run more smoothly. Similarly, give
low priority to many large file downloads so that they do not reduce the quality of other
applications.
Traffic priority will
be automatically
assigned by
Select how the Device assigns priorities to various upstream traffic flows.
•
None:
Disables auto priority mapping and has the Device put packets into the
queues according to your classification rules. Traffic which does not match any of
the classification rules is mapped into the default queue with the lowest priority.
•
Ethernet Priority:
Automatically assign priority based on the IEEE 802.1p priority
level.
•
IP Precedence:
Automatically assign priority based on the first three bits of the
TOS field in the IP header.
•
Packet Length:
Automatically assign priority based on the packet size. Smaller
packets get higher priority since control, signaling, VoIP, internet gaming, or other
real-time packets are usually small while larger packets are usually best effort data
packets like file transfers.
Apply
Click
Apply
to save your changes.
Cancel
Click
Cancel
to restore your previously saved settings.
Summary of Contents for VMG1312-T10C
Page 4: ...Contents Overview VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 4 ...
Page 12: ...Table of Contents VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 12 ...
Page 13: ...13 PART I User s Guide ...
Page 14: ...14 ...
Page 20: ...Chapter 1 Introduction VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 20 ...
Page 28: ...28 ...
Page 34: ...Chapter 4 Connection Status and System Info VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 34 ...
Page 106: ...Chapter 7 Home Networking VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 112 ...
Page 144: ...Chapter 13 Filter VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 152 ...
Page 164: ...Chapter 15 Parental Control VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 172 ...
Page 172: ...Chapter 16 Certificates VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 180 ...
Page 178: ...Chapter 17 System Monitor VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 186 ...
Page 180: ...Chapter 18 User Account VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 188 ...
Page 184: ...Chapter 20 System VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 192 ...
Page 190: ...Chapter 22 Log Setting VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 198 ...
Page 196: ...Chapter 24 Backup Restore VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 204 ...
Page 214: ...Chapter 26 Diagnostic VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 222 ...
Page 232: ...Appendix B Legal Information VMG1312 T10C User s Guide 240 ...






























