Chapter 10 Interfaces
UAG Series User’s Guide
162
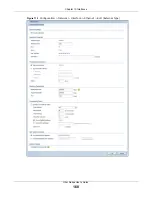
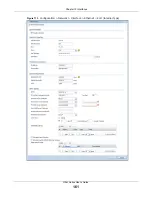
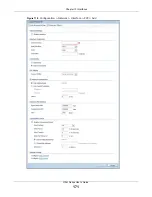
This screen’s fields are described in the table below.
Table 67
Configuration > Network > Interface > Ethernet > Edit
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Show Advanced
Settings / Hide
Advanced Settings
Click this button to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.
General Settings
Enable Interface Select this to enable this interface. Clear this to disable this interface.
Interface Properties
Interface Type
Select to which type of network you will connect this interface. When you select
internal
or
external
the rest of the screen’s options automatically adjust to
correspond. The UAG automatically adds default route and SNAT settings for traffic it
routes from internal interfaces to external interfaces; for example LAN to WAN traffic.
internal
is for connecting to a local network. Other corresponding configuration
options: DHCP server and DHCP relay. The UAG automatically adds default SNAT
settings for traffic flowing from this interface to an external interface.
external
is for connecting to an external network (like the Internet). The UAG
automatically adds this interface to the default WAN trunk.
For
general
, the rest of the screen’s options do not automatically adjust and you must
manually configure a policy route to add routing and SNAT settings for the interface.
Interface Name
Specify a name for the interface. It can use alphanumeric characters, hyphens, and
underscores, and it can be up to 11 characters long.
Port
This is the name of the Ethernet interface’s physical port.
Zone
Select the zone to which this interface is to belong. You use zones to apply security
settings such as security policy control, and remote management.
MAC Address
This field is read-only. This is the MAC address that the Ethernet interface uses.
Description
Enter a description of this interface. It is not used elsewhere. You can use alphanumeric
and
()+/:=?!*#@$_%-
characters, and it can be up to 60 characters long.
IP Address
Assignment
These IP address fields configure an IPv4 IP address on the interface itself. If you
change this IP address on the interface, you may also need to change a related address
object for the network connected to the interface. For example, if you use this screen to
change the IP address of your LAN interface, you should also change the corresponding
LAN subnet address object.
Get
Automatically
This option appears when
Interface Type
is
external
or
general
. Select this to make
the interface a DHCP client and automatically get the IP address, subnet mask, and
gateway address from a DHCP server.
Use Fixed IP
Address
This option appears when
Interface Type
is
external
or
general
. Select this if you
want to specify the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway manually.
IP Address
Enter the IP address for this interface.
Subnet Mask
Enter the subnet mask of this interface in dot decimal notation. The subnet mask
indicates what part of the IP address is the same for all computers in the network.
Gateway
This option appears when
Interface Type
is
external
or
general
. Enter the IP
address of the gateway. The UAG sends packets to the gateway when it does not know
how to route the packet to its destination. The gateway should be on the same network
as the interface.
Metric
This option appears when
Interface Type
is
external
or
general
. Enter the priority of
the gateway (if any) on this interface. The UAG decides which gateway to use based on
this priority. The lower the number, the higher the priority. If two or more gateways
have the same priority, the UAG uses the one that was configured first.
Interface
Parameters