Chapter 38 Access Control
XMG1930 Series User’s Guide
329
38.8.2 SSH Overview
Unlike Telnet or FTP, which transmit data in clear text, SSH (Secure Shell) is a secure communication
protocol that combines authentication and data encryption to provide secure encrypted
communication between two hosts over an unsecured network.
Figure 232
SSH Communication Example
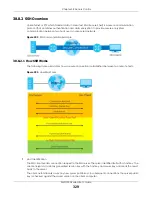
38.8.2.1 How SSH Works
The following table summarizes how a secure connection is established between two remote hosts.
Figure 233
How SSH Works
1
Host Identification
The SSH client sends a connection request to the SSH server. The server identifies itself with a host key. The
client encrypts a randomly generated session key with the host key and server key and sends the result
back to the server.
The client automatically saves any new server public keys. In subsequent connections, the server public
key is checked against the saved version on the client computer.