Chapter 2 IPv6 Address Configuration
Stateless Auto Configuration
Apart from state auto configuration, IPv6 also employs a kind of auto configuration service
named stateless auto configuration.
For the stateless auto configuration, the local link must support multicast. The network
interface must be able to send and receive multicast packets.
In the stateless auto
configuration process, the relevant nodes must meet the following requirements.
l
A node for auto configuration must determine its own link-local address.
l
Authenticate this link-local address to make sure that it is unique in the link.
l
The node must determine the information to be configured. Such information can be
the IP address of this node, other configuration information, or both of them. In case
an IP address is needed, the node must determine whether to obtain it through the
stateless auto configuration or through the state auto configuration.
The procedure is as follows:
1.
In the stateless auto configuration process, the host adds its network adapter MAC
address after the 1111111010 prefix of the link-local address to create a link-local
unicast address.
IEEE has modified the network adapter MAC address from 48-bit to 64-bit. If the
network adapter MAC address used by the host is still 48-bit, the IPv6 network adapter
driver will convert the 48-bit MAC address to the 64-bit MAC address in accordance
with an IEEE formula.
2.
The host sends a neighbor discovery request to the address to check whether the
address is unique.
If there is no response to the request, it indicates that the link-local unicast address
configured by the host itself is unique. Otherwise, the host will use an interface ID
randomly created to form a new link-local unicast address.
3.
Taking the address as the source address, the host sends a router solicitation in the
multicast way to all the routers within the local link to request configuration information.
Routers respond to it with a router advertisement containing the prefix of an aggregable
global unicast address and other relevant configuration information.
The host automatically uses the global address prefix obtained from routers and its
own interface ID to automatically configure a global address to communicate with other
hosts within the Internet.
2.2 Configuring an IPv6 Address
This procedure describes how to configure an IPv6 address for an interface, which is the
prerequisite for managing and configuring other functions.
Steps
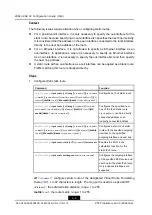
1.
Configure IPv6 address.
2-13
SJ-20140504150128-018|2014-05-10 (R1.0)
ZTE Proprietary and Confidential