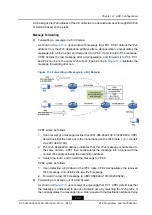
Chapter 16 IPv6 Tunnel Configuration
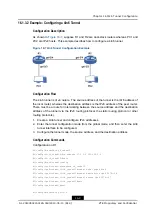
interface v6_tunnel2
tunnel mode ipv6ip 6to4
tunnel source ipv4 1.1.1.1
! </ipv6-tunnel>
R1(config)#show ipv6 interface brief
v6_tunnel2
[up/up]
fe80::101:101
2002:101:101:1::1/64
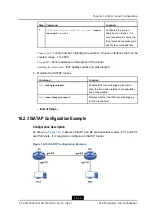
16.2 ISATAP Tunnel Configuration
16.2.1 ISATAP Tunnel Overview
ISATAP Tunnel Introduction
With the wide applications of IPv6 technology, there are more IPv6 hosts on the
current IPv4 network. Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (
) tunnel
technology provides a good solution for such application.
ISATAP can obtain the
destination of a tunnel automatically by embedding an IPv4 address in the destination
address of an IPv6 packet.
When an ISATAP tunnel is used, the destination address of an IPv6 packet and the IPv6
address of a tunnel interface should use special ISATAP addresses. The format of an
ISATAP address is Prefix (64 bit):0:5EFE:ip-address. The 64-bit prefix is the prefix of a
legal IPv6 unicast address, and the ip-address is a 32-bit IPv4 source address (in the
a.b.c.d format or abcd:efgh format). Through this embedded IPv4 address, a tunnel can
be established automatically to transmit IPv6 packets. ISATAP tunnels are mainly used to
establish connections between IPv6 routers, and between IPv6 hosts and IPv6 routers on
the IPv4 network.
ISATAP Tunnel Work Flow
ISATAP encapsulation and decapsulation are described below.
l
Encapsulation principle: When an IPv6 is sent, the egress is an tunnel interface. The
tunnel type is determined according to packet call-back on the interface. If it is an
ISATAP tunnel, IPv4 header encapsulation is performed. An ISATAP tunnel follows the
encapsulation format of a 6in4 tunnel. The outer IPv4 destination address is the IPv4
address embedded in the destination address of the IPv6 packet, and the outer IPv4
source address is the source address of the ISATAP tunnel. After the encapsulation,
the packet is handled according to the common IPv4 packet sending flow.
l
Decapsulation principle: The decapsulation flow of an ISATAP tunnel is the same as
that of a 6in4 tunnel. When an IPv4 packet is received and the protocol number in
the IPv4 header is 41, the protocol number processing functions registered for IPv4
are called and the 6in4 decapsulation function is used. The device searches for the
matched tunnel entity according to the source address and destination address of
16-13
SJ-20140504150128-018|2014-05-10 (R1.0)
ZTE Proprietary and Confidential