FORM 155.32-ICOM2.EN.UL
SECTION 2 - PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
ISSUE DATE:1/10/2018
JOHNSON CONTROLS
19
PLATE TYPE HEAT EXCHANGERS
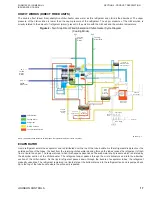
The dilute (weak) LiBr solution leaving the absorber section is pumped through various
plate type heat exchangers (such as the low temperature heat exchanger, LTG refrigerant
condensate heat exchanger, and high temperature heat exchanger) before it enters the
high temperature generator and low temperature generator sections. These plate type heat
exchangers provide cycle efficiency by preheating the dilute solution. Preheating the dilute
solution reduces the consumption of the driving heat source in the high temperature
generator section. The concentrated solution flows out of the generators and back through
the heat exchangers.
The relatively high temperature solution streams from the two generators are used to pre-
heat the weak solution stream leaving the absorber.
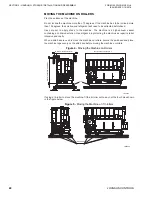
PARALLEL FLOW
The unique parallel flow divides the solution between the low temperature generator and
the high temperature generator sections into two parallel, balanced paths. The result is a
safer and more efficient operation at a much lower pressure than conventional series-flow
designs. The various solution-to-solution plate type heat exchangers optimize efficiency by
enabling effective heat transfer between the diluted (weak) and the concentrated LiBr
solutions.
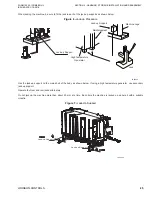
HIGH TEMPERATURE GENERATOR (HTG)
YHAU’s high temperature generator has the unique liquid tube design in which the dilute
LiBr solution coming from the high temperature heat exchanger is inside the tubes. The
products of combustion (exhaust gas from burning of natural gas) are on the shell side. The
hot refrigerant vapor boiled off is sent to the low temperature generator. This leaves behind
a strong solution which is returned through the high temperature heat exchanger.
The liquid tube design is efficient and compact with lower pressure drop as compared to
the conventional smoke tube type design in which the exhaust gas is inside the tubes while
the LiBr solution is on the shell side. Being more efficient, the exhaust gas leaving
temperature is lower than the smoke tube design.
The liquid tube design also benefits from less volume of LiBr solution and hence faster
startup time. It does not require any ceramic refractory compared to the conventional
design, therefore improved reliability.
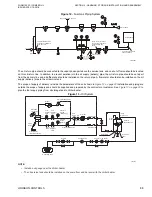
LOW TEMPERATURE GENERATOR (LTG)
The hot refrigerant vapor from the high temperature generator heats up the dilute solution
coming in from the low temperature heat exchanger. This vapor then condenseses into hot
refrigerant liquid and is sent to the condenser via the drain heat exchanger. The additional
vapor produced in the LTG by heating up the dilute solution is sent to the condenser.
The LTG is of a falling film design, ensuring superior heat transfer and enhanced life by
eliminating wear and tear at the tube supports.
Concentrated
Solution In
Dilute
Solution In
Low Temp.
Heat Exchanger
)UTIKTZXGZKJ
9UR[ZOUT5[Z
*OR[ZK
9UR[ZOUT5[Z