2
Examples of Use of Relative Jobs
DX100
2.1
Shift Function to Offset Workpiece Position Error
2-1
156191-1CD
HW0482494
2
Examples of Use of Relative Jobs
2.1
Shift Function to Offset Workpiece Position Error
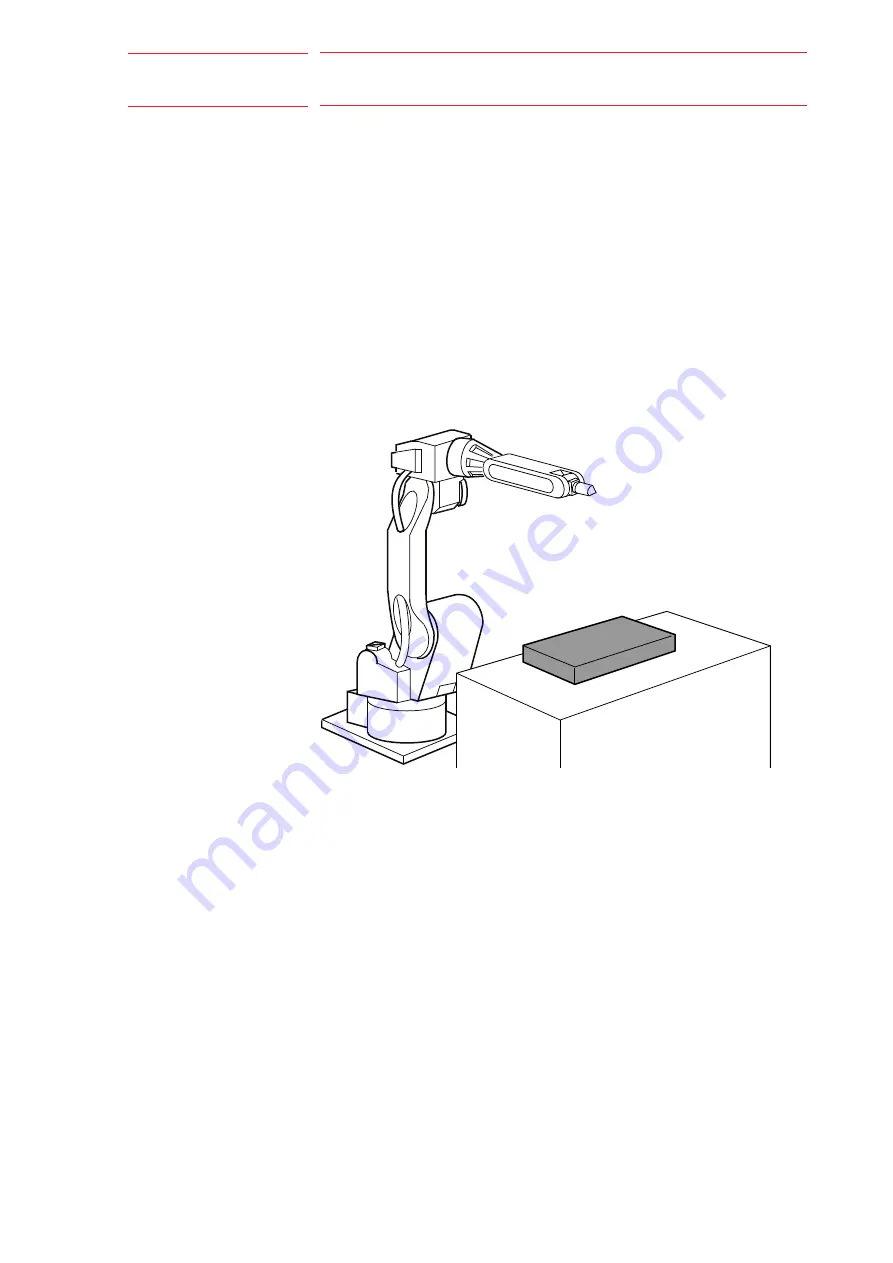
After teaching a standard job for a workpiece placed at a reference point,
the job is converted into a relative job in a user coordinate system. With a
shift function and sensors, possible differences of workpiece positions
between teaching and playback can be offset.
1. Place a workpiece at a reference point and teach as usual. Name the
job as “STANDARD-1”.
11/63