Table 5.11 Differences between Heavy and Normal Duty
Mode
Heavy Duty Rating (HD)
Normal Duty Rating (ND)
C6-01
0
1
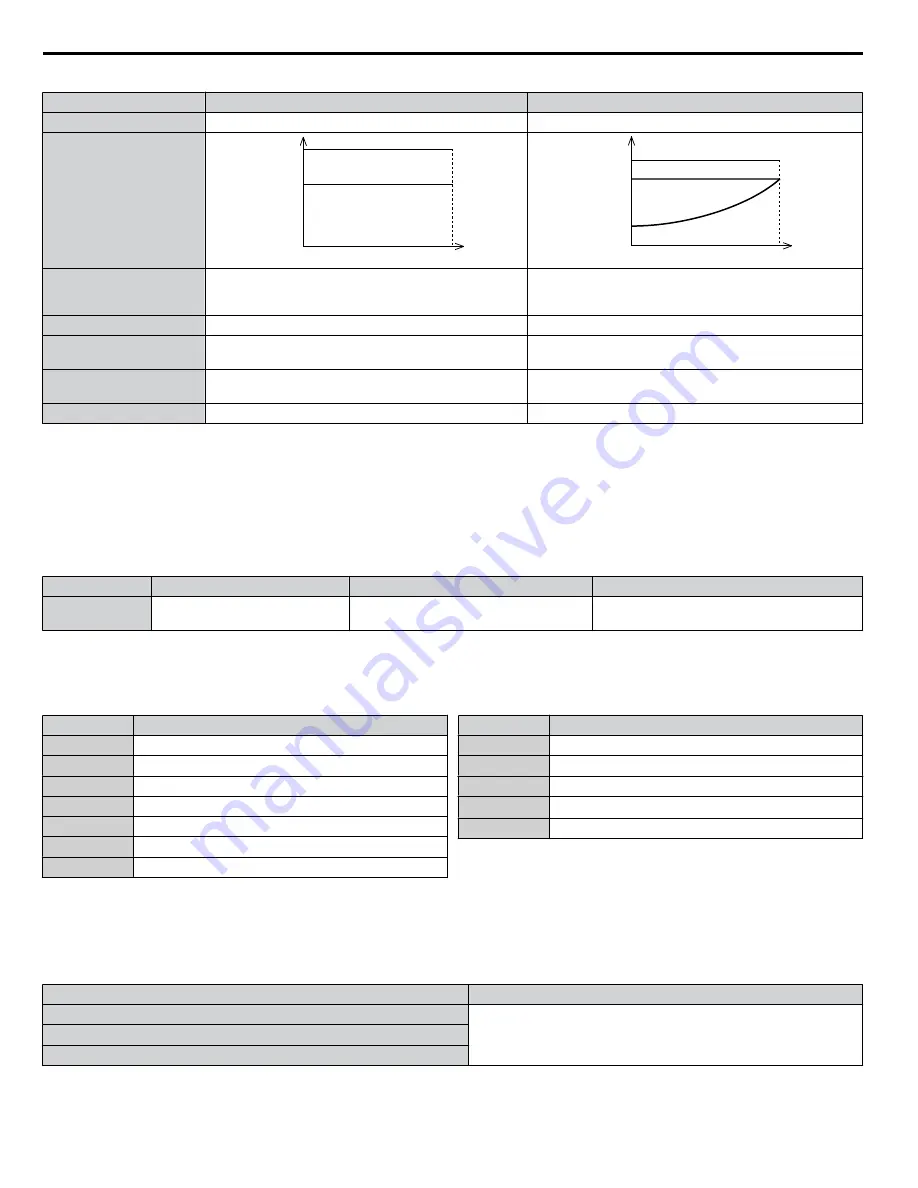
Characteristics
100 %
100 %
0
Motor Speed
Rated Load
Overload
150 %
Motor Speed
0
100 %
100 %
120 %
Rated Load
Overload
Application
Use Heavy Duty Rating for applications requiring a high
overload tolerance with constant load torque. Such
applications include extruders and conveyors.
Use Normal Duty Rating for applications in which the torque
requirements drop along with the speed. Examples include
fans or pumps where a high overload tolerance is not required.
Over load capability (oL2)
150% of drive rated Heavy Duty current for 60 s
120% of drive rated Normal Duty current for 60 s
L3-02 Stall Prevention
during Acceleration
150%
120%
L3-06 Stall Prevention
during Run
150%
120%
Default Carrier Frequency
8/10 kHz
2 kHz Swing PWM
Note:
By changing the Drive Duty, the drive maximum applicable motor power changes and the E2-
oo
and E4-
oo
parameters are automatically
set to appropriate values.
n
C6-02: Carrier Frequency Selection
Parameter C6-02 sets the switching frequency of the drive’s output transistors. It can be changed in order to reduce audible
noise and also reduce leakage current.
Note:
The drive rated current is reduced when the carrier frequency is set higher than the default value.
Refer to Rated Current Depending on
No.
Parameter Name
Setting Range
Default
C6-02
Carrier Frequency Selection
<1>
Determined by A1-02 and o2-04.
Reset when C6-01 is changed.
<1> Setting range is determined by the drive software version.
PRG: 1020 and later: 1 to B; F
PRG: 1018 and earlier: 1 to A; F
Settings:
C6-02
Carrier Frequency
1
2.0 kHz
2
5.0 kHz
3
8.0 kHz
4
10.0 kHz
5
12.5 kHz
6
15.0 kHz
7
Swing PWM 1
C6-02
Carrier Frequency
8
Swing PWM 2
9
Swing PWM 3
A
Swing PWM 4
B
<1>
Leakage Current Rejection PWM
F
User-defined (C6-03 to C6-05)
<1> Available in drive software versions PRG: 1020 and later. Setting B uses a PWM pattern that reduces the amount of leakage current detected over
long wiring distances. This can help reduce alarm detection and problems with the current monitor that result from leakage current over long wiring
distances. This is the same as setting the carrier frequency to 2 kHz.
Note:
Swing PWM uses 2.0 kHz carrier frequency as a base. Applying special PWM patterns minimizes the audible noise of the motor.
Guidelines for Carrier Frequency Parameter Setup
Symptom
Remedy
Speed and torque are unstable at low speeds.
Lower the carrier frequency.
Noise from the drive is affecting peripheral devices.
Excessive leakage current from the drive.
5.3 C: Tuning
156
YASKAWA ELECTRIC SIEP C710606 18F YASKAWA AC Drive – V1000 Technical Manual
















































