TH250
Programmer’s Guide
78
Status
Status command introduction
The TH250 has three methods of providing status to the application. These methods are through
batch status commands, real time status commands and unsolicited status mode. An application
may use one or more of these methods to understand the current status of the printer. A brief
description of each of these methods follows.
Batch status commands – These commands are sent to the printer and stored in the printer’s
buffer. Once the printer has processed all the previous commands these commands are processed
and the proper status is returned to the application. In the event a condition causes the printer to
go BUSY, it stops processing commands from the printer buffer. If a batch status command
remained in the buffer during this busy condition, it would not be processed. In fact, no batch
commands are processed while the printer is in this state.
Real-time commands – These commands are sent to the printer buffer. Periodically, when the
printer has time, it scans the input buffer looking for these commands. When found by the printer,
these commands are processed immediately. This gives the application the ability to query the
printer when it is in a busy state in order to correct whatever fault has occurred.
Automatic status back or Unsolicited status mode– This mechanism allows the application
developer to program the printer to automatically respond with a four byte status when certain
conditions in the printer change.
Please see the subsequent sections for a more detailed description of these status commands. At
the end of this status commands section is a page entitled “Recognizing data from the printer”.
This describes how to interpret what command or setting (in the case of unsolicited status mode)
triggered a response from the printer.
Batch mode
For RS-232C printers, these commands enable the printer to communicate with the host computer
following the selected handshaking protocol, either DTR/DSR or XON/XOFF. They are stored in the
printer’s data buffer as they are received, and are handled by the firmware in the order in which
they are received.
When a fault occurs, the printer will go busy at the RS-232C interface and not respond to any of
the batch mode printer status commands. If the fault causing the busy condition can be cleared,
such as by loading paper, or letting the thermal printhead cool down, the printer will resume
processing the data in its receive buffer.
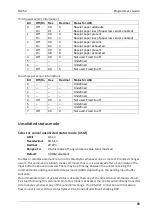
Transmit peripheral device status (RS-232C printers only)
ASCII
ESC u 0
Hexadecimal
1B 75 0
Decimal
27 117 0
Value of returned byte:
Bit 0
Bit 1
1 = Drawer 1 Closed
1 = Drawer 2 Closed
0 = Drawer 1 Open
0 = Drawer 2 Open
Summary of Contents for TH250
Page 1: ...TH250 Thermal Printer Programmer s Guide January 2016 ...
Page 153: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 148 Character code table Page 1 PC850 Multilingual Latin I ...
Page 154: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 149 Character code table Page 2 PC852 Latin II ...
Page 155: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 150 Character code table Page 3 PC860 Portuguese ...
Page 156: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 151 Character code table Page 4 PC863 Canadian French ...
Page 157: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 152 Character code table Page 5 PC865 Nordic ...
Page 158: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 153 Character code table Page 6 PC858 Multilingual I Euro ...
Page 159: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 154 Character code table Page 7 PC866 Russian ...
Page 160: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 155 Character code table Page 8 WPC1252 Latin I ...
Page 161: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 156 Character code table Page 9 PC862 Hebrew ...
Page 162: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 157 Character code table Page 10 PC737 Greek ...
Page 163: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 158 Character code table Page 11 PC874 Thai ...
Page 164: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 159 Character code table Page 12 PC857 Turkish ...
Page 165: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 160 Character code table Page 13 WPC1251 Cyrillic ...
Page 166: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 161 Character code table Page 14 WPC1255 Hebrew ...
Page 167: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 162 Character code table Page 15 KZ_1048 Kazakh ...
Page 168: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 163 Character code table Page 16 WPC1254 Turkish ...
Page 169: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 164 Character code table Page 17 WPC1250 Central Europe ...
Page 170: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 165 Character code table Page 18 WPC28591 Latin 1 ...
Page 171: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 166 Character code table Page 19 WPC28592 Latin 2 ...
Page 172: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 167 Character code table Page 20 WPC28599 Turkish ...
Page 173: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 168 Character code table Page 21 WPC28605 Latin 9 ...
Page 174: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 169 Character code table Page 22 PC864 Arabic ...
Page 175: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 170 Character code table Page 23 PC720 Arabic ...
Page 176: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 171 Character code table Page 24 WPC1256 Arabic ...
Page 177: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 172 Character code table Page 25 WPC28596 Arabic ...
Page 178: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 173 Character code table Page 26 KATAKANA Asia ...
Page 179: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 174 Character code table Page 27 PC775 Baltic ...
Page 180: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 175 Character code table Page 28 WPC1257 Baltic ...
Page 181: ...TH250 Programmer s Guide 176 Character code table Page 29 WP28594 Baltic ...