MANAGING STORAGE
54
MY CLOUD USER MANUAL
Viewing the Current RAID Mode
Use the following steps to view the RAID mode currently used on your device.
1. On the Navigation bar, click
Storage
to display the Storage screen.
2. Click
RAID
, if not already selected.
3. In the RAID Profile and RAID Volume areas, the following information displays:
RAID Health.
Auto-Rebuild status (whether or not Auto Rebuild is turned on).
RAID Volume which shows the number of volumes for which RAID or JBOD are
configured.
Changing the RAID Mode
Use the following steps to change the current RAID mode on your My Cloud device.
1. On the Navigation bar, click
Storage
to display the Storage screen.
2. Click
RAID
, if not already selected.
3. Click
Change RAID Mode
at the bottom of the screen.
4. Review the warning message and click
OK
.
5. Select the RAID mode you’d like to use for your My Cloud device.
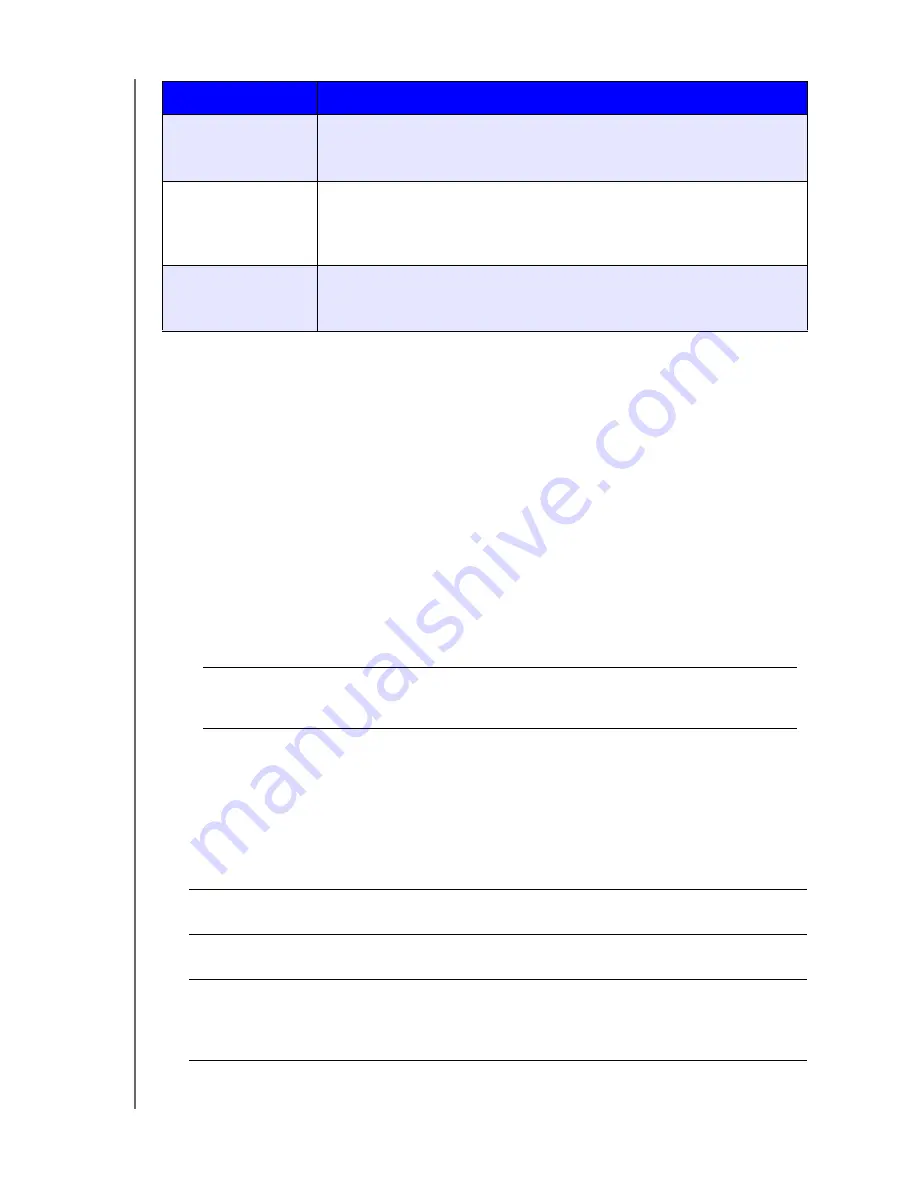
Options include:
RAID 1
In RAID 1 mode, the RAID controller duplicates all data from one drive to a
second drive in the drive group. RAID 1 provides complete data redundancy,
but cuts the required storage capacity in half.
RAID 5
RAID 5 mode offers superior performance and protection by striping data
across 3 or more drives and dedicating a quarter of each drive to fault
tolerance.
This option is only available for 4-bay My Cloud devices.
RAID 10
RAID 10 mode is a RAID protocol in which data is written in stripes across
primary disks that have been mirrored to the secondary disks.
This option is only available for 4-bay My Cloud devices.
WARNING!
Changes made to your RAID mode will delete all of your data and
your user settings. See “Saving a Configuration File” on page 88 for
information on saving your user settings.
JBOD
The use of one or more drives not in a RAID configuration but
managed as separate logical volumes.
Spanning
Combination of drives in a linear fashion to create one large
logical volume.
RAID 0
Data is striped across multiple hard drives, enabling accelerated
reading and recording of data by combining the work of two or
more drives to increase performance.
However, If one drive fails, all of your data will be lost.
RAID Mode
Description






























