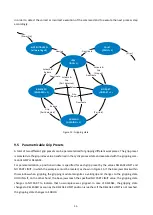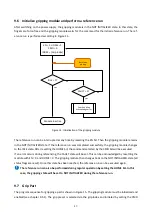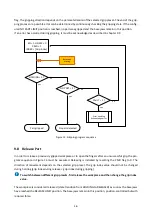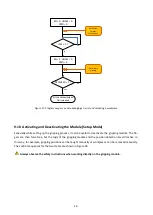
41-
EN = 1, HOME = 0
CMD = 0
INDEX = [Grip Index]
RELEASED = 1 ?
no
yes
Module active and
open
Base Jaws
moving
EN = 0, HOME = 0
CMD = 0
INDEX = 0
IDLE = 1 ?
no
yes
Module inactive
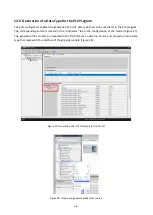
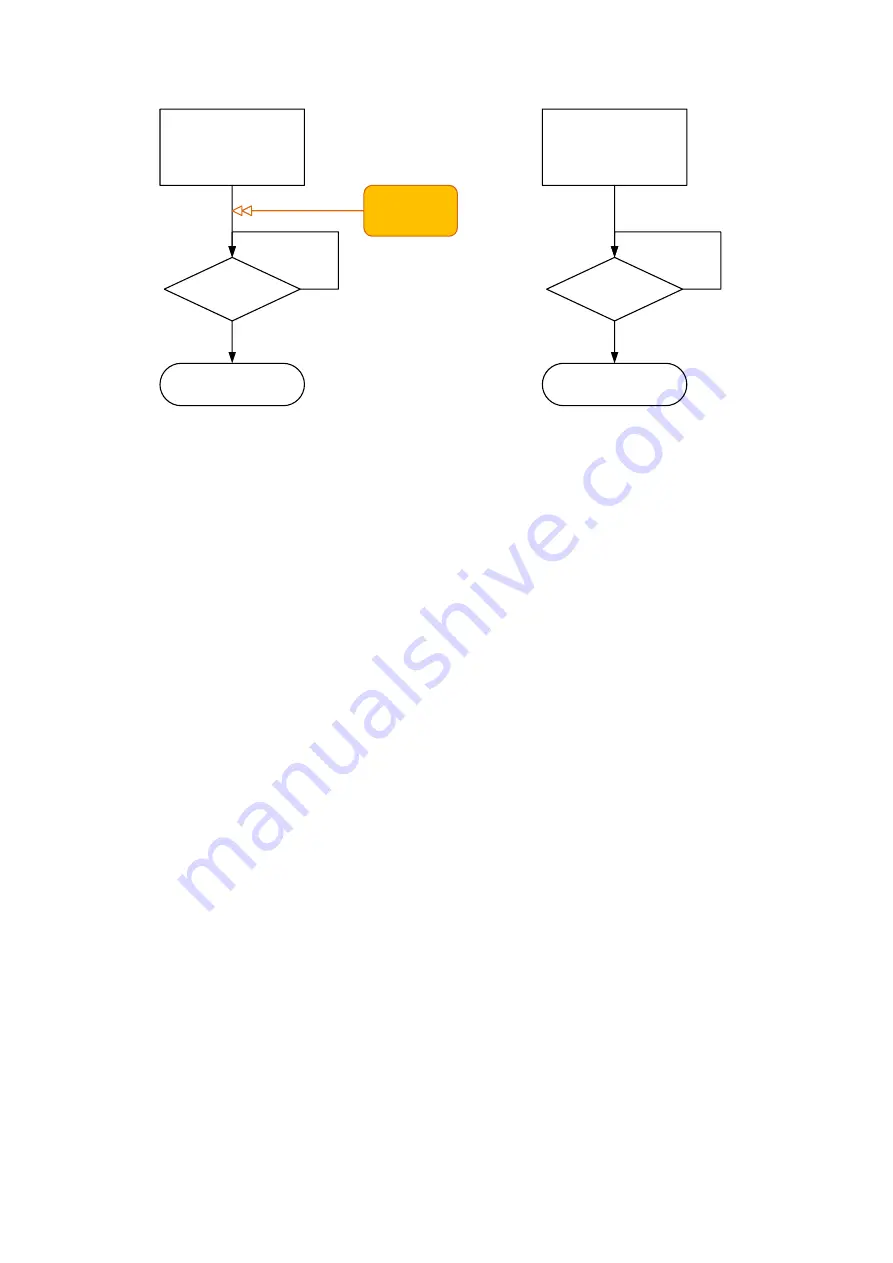
Figure 18: Activating (left) and deactivating (right) the gripping module program sequence
9.11
Design of the Gripping Process
The design of the gripping process is decisive for the reliability of the production process. The following points
have proven to be helpful:
•
Place the gripping point in the center of the stroke range of the base jaws by constructively designing
the fingers, if the process allows it.
•
If possible, secure the position of the workpiece by establishing a form-fit connection between the
fingers and the workpiece.
•
Avoid inaccuracies in the contact with the part by constructing the contact areas accordingly.
•
Use a compensatory element if lateral forces can occur on the gripping module due to gripping or
positioning tolerances. This is the case, for example, if a clamped workpiece is to be picked up by a
gripping module positioned by a robot.
•
Choose a sufficiently large gripping range (recommended distance between RELEASE LIMIT and NO
PART LIMIT
≥
2 mm) to maximize the reliability of the gripping process.
•
Always maintain a distance to the inner and outer limit with the positions for RELEASE LIMIT and NO
PART LIMIT, so that a safe detection of the grip is possible and the gripping module does not grip itself.
•
During holding, the continuous application of the gripping force generates heat that must be dissipated
from the gripping module. Make sure that the mounting surface has sufficient heat dissipation. Avoid
permanent holding and do not block the fingers beyond the actual gripping process (e.g. by setting the
RELEASE LIMIT value outside the stroke range) in order not to heat up the module unnecessarily..
•
Perform some empty strokes over the entire range of motion every 1000 gripping cycles to distribute
the lubricant in the linear guides.
The following application examples describe the implementation of simple handling tasks and the associated
parameterization and use of the gripping module via IO-Link.