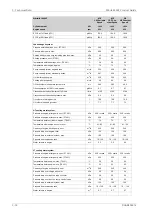
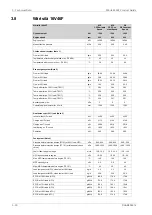
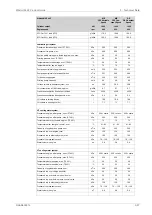
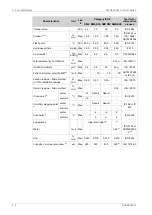
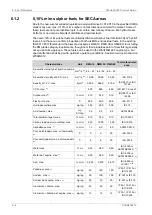
Max velocity [m/s]
Pipe material
Piping
2.5
Galvanized steel
Sea water piping
2.5
Aluminium brass
3.0
10/90 copper-nickel-iron
4.5
70/30 copper-nickel
4.5
Rubber lined pipes
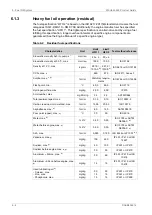
Compressed air pipe sizing has to be calculated project specifically. The pipe sizes may be
chosen on the basis of air velocity or pressure drop. In each pipeline case it is advised to
check the pipe sizes using both methods, this to ensure that the alternative limits are not being
exceeded.
Pipeline sizing on air velocity:
For dry air, practical experience shows that reasonable
velocities are 25...30 m/s, but these should be regarded as the maximum above which noise
and erosion will take place, particularly if air is not dry. Even these velocities can be high in
terms of their effect on pressure drop. In longer supply lines, it is often necessary to restrict
velocities to 15 m/s to limit the pressure drop.
Pipeline sizing on pressure drop:
As a rule of thumb the pressure drop from the starting air
vessel to the inlet of the engine should be max. 0.1 MPa (1 bar) when the bottle pressure is 3
MPa (30 bar).
It is essential that the instrument air pressure, feeding to some critical control instrumentation,
is not allowed to fall below the nominal pressure stated in chapter "Compressed air system"
due to pressure drop in the pipeline.
5.2
Trace heating
The following pipes shall be equipped with trace heating (steam, thermal oil or electrical). It
shall be possible to shut off the trace heating.
●
All heavy fuel pipes
●
All leak fuel and filter flushing pipes carrying heavy fuel
5.3
Pressure class
The pressure class of the piping should be higher than or equal to the design pressure, which
should be higher than or equal to the highest operating (working) pressure. The highest
operating (working) pressure is equal to the setting of the safety valve in a system.
The pressure in the system can:
●
Originate from a positive displacement pump
●
Be a combination of the static pressure and the pressure on the highest point of the pump
curve for a centrifugal pump
●
Rise in an isolated system if the liquid is heated
Within this publication there are tables attached to drawings, which specify pressure classes
of connections. The pressure class of a connection can be higher than the pressure class
required for the pipe.
Example 1:
The fuel pressure before the engine should be 0.7 MPa (7 bar). The safety filter in dirty condition
may cause a pressure loss of 0.1 MPa (1.0 bar). The viscosimeter, automatic filter, preheater
and piping may cause a pressure loss of 0.25 MPa (2.5 bar). Consequently the discharge
5-2
DAAB605814
Wärtsilä 46F Product Guide
5. Piping Design, Treatment and Installation
Summary of Contents for 46F Series
Page 1: ...Wärtsilä 46F PRODUCT GUIDE ...
Page 4: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 8: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 18: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 86: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 104: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 154: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 162: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 170: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 176: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 194: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 200: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 202: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
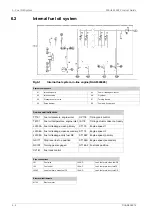
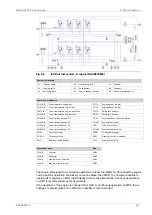
Page 207: ...Fig 21 7 List of symbols DAAF406507 7 DAAB605814 21 5 21 ANNEX Wärtsilä 46F Product Guide ...