38 • vacon
Description of parameters
Tel. +358 (0)201 2121 • Fax +358 (0)201 212 205
Par. ID510
Par. ID509
Par. ID518 = 0,2
Par. ID518 = 1,2
NX12k81
fout [Hz]
Time [s]
515
DC-braking
frequency
at stop
(2.4.5)
The output frequency at which the DC-braking is applied. See Figure 16.
516
DC-braking
time
at
start
(2.4.6)
DC-brake is activated when the start command is given. This parameter defines the time
before the brake is released. After the brake is released, the output frequency increases
according to the set start function by parameter
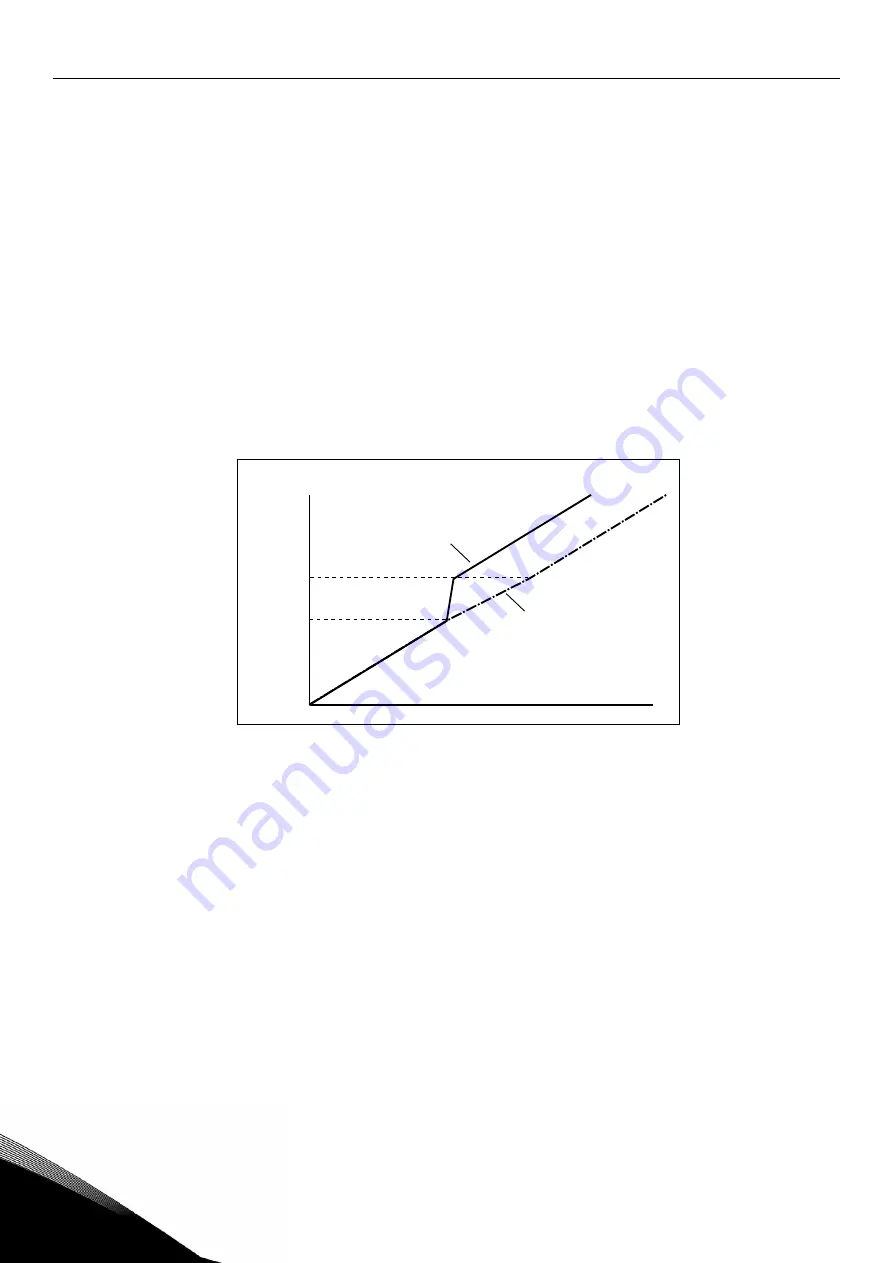
518
Acceleration/deceleration ramp speed scaling ratio between prohibit frequency limits
23457
(2.5.3,
2.5.7)
Defines the acceleration/deceleration time when the output frequency is between the selected
prohibit frequency range limits (parameters
). The ramping speed (selected
acceleration/ deceleration time 1 or 2) is multiplied with this factor. E.g. value 0.1 makes the
acceleration time 10 times shorter than outside the prohibit frequency range limits.
Figure 17. Ramp speed scaling between prohibit frequencies
519
Flux
braking
current
(2.4.8)
Defines the flux braking current value. The value setting range depends on the used
application.
520
Flux
brake
(2.4.7)
Instead of DC braking, flux braking is a useful way to raise the braking capacity in cases where
additional brake resistors are not needed.
When braking is needed, the frequency is reduced and the flux in the motor is increased, which
in turn increases the motor's capability to brake. Unlike DC braking, the motor speed remains
controlled during braking.
The flux braking can be set ON or OFF.
0 = Flux braking OFF
1 = Flux braking ON
Note: Flux braking converts the energy into heat at the motor, and should be used
intermittently to avoid motor damage.
















































