35
3.3.1 SATA Port 1~6/Ext. Primary Master/Slave
Computer detects the hard disk drive type for each drive.
Press [Enter] to view advanced details of the corresponding drive.
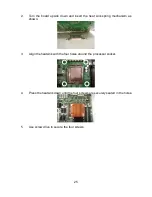
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main
Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Item Specific Help
Type:
Multi-Sector Transfers:
LBA Mode Control:
32 Bit I/O:
Transfer Mode:
Ultra DMA Mode:
[
Auto]
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
[Standard]
[Disabled]
User = your enter
parameters of hard-disk
drive installed at this
connection.
Auto = autotypes hard-
disk drive installed here.
1-39 = you select pre-
determined type of
hard-disk drive installed
here.
CD-ROM = a CD-ROM
drive is installed here.
ATAPI Removable =
removable disk drive is
installed here.
F1
Help
↑↓
Select Item
-/+
Change Values
F9
Setup Defaults
Esc
Exit
←
→
Select Menu
Enter
Select
X
Sub-Menu
F10
Save and Exit
The system displays advanced details like the number of heads/cylinders/sectors on
the detected disk and the maximum storage capacity of the disk.
This option lets you set the following hard disk parameters:
Type
Selects the type of device connected to the system.
Options:
Auto
/ CD/DVD / Not Installed / ARMD
Multi-Sector Transfers
This option allows you to specify the number of sectors per block for multiple sector
transfers.
Options: Disabled / 2 Sectors / 4 Sectors / 8 Sectors /
16 Sectors
LBA Mode Control
Enables or disables LBA Mode.
When LBA is turned on, the BIOS will enable geometry translation. This translation
may be done in the same way that it is done in Extended CHS or large mode, or it
may be done using a different algorithm called LBA-assist translation. The
translated geometry is still what is presented to the operating system for use in Int
13h calls. The difference between LBA and ECHS is that when using ECHS the
BIOS translates the parameters used by these calls from the translated geometry to
the drive's logical geometry. With LBA, it translates from the translated geometry
directly into a logical block (sector) number.
Options: Disabled /
Enabled