52
Operating principle
In the electrode boiler humidifier, the current flowing between the electrodes in the water in the cylinder generates the
heat necessary to boil the water.
By controlling the water level and the concentration of salt measured in the steam cylinder (U1) using the feed water
solenoid valve (U8) and the boiler cylinder electric drainage valve (U9), the electric current is regulated by means of an
amperometric transformer (U11).
When steam is needed, the humidifier contact is closed (see the electrical diagram) which provides power to the
immersed electrodes. When the current falls below the value required as a result of the fall in the water level, the feed
water solenoid valve is opened (U8).
the boiler cylinder electric drainage valve (U9) is opened at intervals depending on the characteristics of the feed water
supply in order to maintain the optimum concentration of dissolved salts in the water in the cylinder (U1).
Feed water
Values for the feed water for medium-high level of conductibility of a humidifier with immersed electrodes.
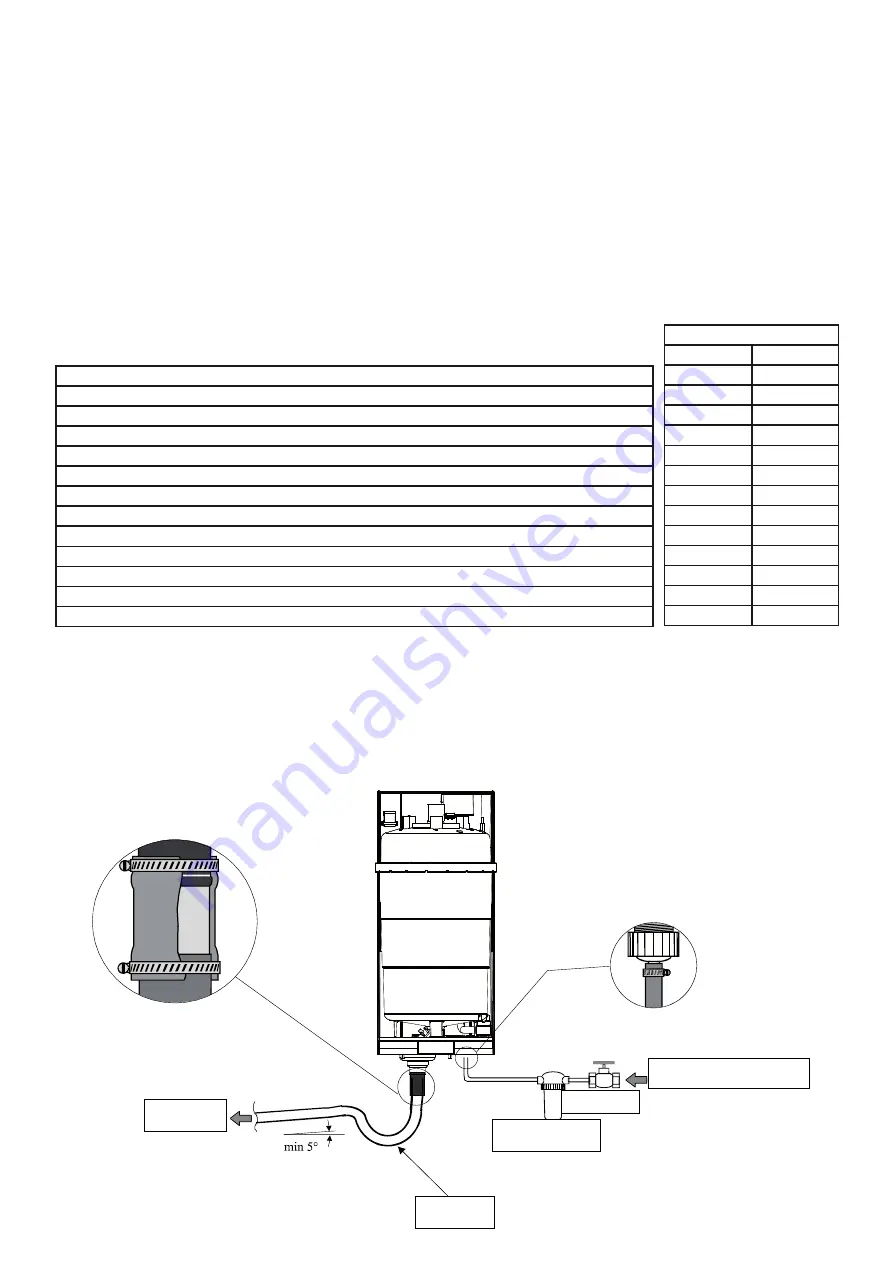
Connections
The installation of the humidifier requires connection to the feed tubes of the water drain.
(1) Values dependent on the specific conductibility; in general: TDS @ 0,93 * s20; R180 @ 0,65 * s20
(2) not lower than 200% of the Chloride content in mg/l di Cl-
(3) not lower than 300% of the Chloride content in mg/l di Cl-
Hydrogen ion activity
pH
-
Specific conductibility at 20 °C
, 20 °C
-
µS/cm
total dissolved solids
tDS
-
mg/l
Residual fixed at 180 °C
r180
-
mg/l
total hardness
tH
-
mg/l CaCo3
temporary hardness
-
mg/l CaCo3
iron + Manganese
-
mg/l Fe + Mn
Chlorides
-
ppm Cl
Silica
-
mg/l Sio2
residual chloride
-
mg/l Cl-
Calcium sulphate
-
mg/l CaSo4
Metallic impurities
-
mg/l
Solvents, dilutents, soaps, lubricants
-
mg/l
Feed tubes
Siphon
Filter
Drain
valve
LiMitS
Min.
Max.
7
8.5
300
1250
(
1
)
(
1
)
(
1
)
(
1
)
100(
2
)
400
60(
3
)
300
0
0.2
0
30
0
20
0
0.2
0
100
0
0
0
0









































