0-7
SI UNITS
Meaning of SI
This manual uses SI units. SI represents the International System of Units, which was established to unify
the various systems of units used in the past for smoother international technical communication.
New Units Adopted in SI
<Reference>
* 1: X represents the value in SI units as converted from 1 [in conventional units], which can be
used as the rate for conversion between conventional and SI units.
* 2: In the past, kilogram [kg] representing mass was often used in place of weight kilogram [kgf],
which should be used as the unit of force.
Conversion between Conventional and SI Units
Equation for conversion
When converting, change the unit of the value in conventional or SI units to the one in the
conversion rate column in the table above before calculation. For example, when converting 100 W
to the value in conventional unit PS, first change it to 0.1 kW and divide by the conversion rate
0.735499.
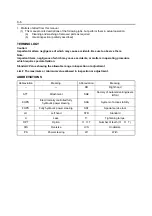
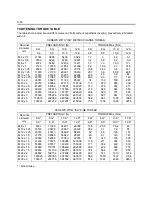
Item
New unit
Conventional
unit
Conversion rate*
1
(1 [conventional unit] = X [SI
unit])
Force*
2
N (newton)
kgf
1 kgf = 9.80665 N
Torque
*2
(Moment)
N·m
kgf·cm
1 kgf·cm = 9.80665 N·m
Pressure*
2
Bar
kgf/cm
2
1 Bar = 1 kgf / cm
2
Pressure*
2
Pa (pascal)
kgf/cm
2
1 kgf/cm
2
= 98.0665 kPa = 0.0980665 MPa
↑
↑
mmHg
1 mmHg = 0.133322 kPa
Revolving speed
rpm
rpm
1 rpm = 1 r/min
Spring con-
N/mm
kgf/mm
1 kgf/mm = 9.80665 N/mm
Volume
l
cc
1 cc = 1 m
l
Power
W
PS system
1 PS = 0.735499 kW
Heat quantity
W·h
cal
1 kcal = 1.16279 W·h
Specific fuel
g/W·h
g/PS·h
1 g/PS·h = 1.3596 g/kW·h
Value in SI unit = Conversion rate
×
Value in conventional unit
Conversion rate: Figure corresponding
to X in the conversion rate column in
the table above
Value in conventional unit = Value in SI unit
÷
Conversion rate