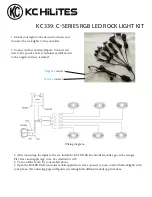
© 2007 - 2018 Thorlabs
116
Wavefront Sensor
8.6 Example Zernike Calculations
Example Tilt:
Q:
How can the linear wavefront tilt in x direction be derived from a measured Zernike coeffi-
cient of Z3 = 0.1 µm at a pupil diameter of 4 mm?
A:
With a normalization factor of 2 the wavefront shape
WF(x)
in Cartesian coordinates is:
WF(x) = 0.1 µm*2*x
Since the normalized x coordinate ranges from -1 to +1 within the unit circle, the maximum
wavefront deviation is therefore -0.2 µm at x = -1 and 0.2 µm at x = 1.
That is, we have a total tilt of 0.4 µm across the entire physical pupil diameter of 4 mm which
gives a tilt angle of
arctan
(0.4 µm / 4 mm) = 0.1 mrad = 0.0057 deg.
Example Defocus:
Q1
: What peak-to-valley (PV) deformation corresponds to a Defocus term of Z5 = -1 µm?
A1
: As the pure mathematical defocus formula (2r
2
- 1) describes a concave wavefront, the
wavefront shape
WF(
r
)
in polar coordinates is:
WF(
r
r
2-1)
Since the normalized radial coordinate
r
ranges from 0 to 1 and the spherical shape achieves
its minimum and maximum wavefront deviation at these points, the PV value is just the differ-
ence
PV=WF(
r
=0) – WF(
r
This PV result is independent of the physical pupil diameter because it just describes the wave-
front deviation in z direction.
Q2
: What Radius of Curvature (RoC) is related to this spherical wavefront when measured at
a pupil diameter of d = 3 mm?
A2
: To convert the PV value into a RoC result, a standard mathematimatical circle function is
used. In
under ‘Sagitta’ the following formula is given:
146
Summary of Contents for WFS20-14AR
Page 2: ...Copyright 2007 2018 Thorlabs Version Date 5 0 19 Jul 2018...
Page 15: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 3 Coordinate Definitions 13 Wavefront Graph...
Page 106: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 104 Wavefront Sensor Selectable camera image sizes for WFS40 Normal Mode...
Page 107: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 105 Selectable camera image sizes for WFS40 sub2 Mode...
Page 123: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 121 8 9 2 Drawing WFS20 5C...
Page 124: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 122 Wavefront Sensor 8 9 3 Drawing WFS20 5C M...
Page 125: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 123 8 9 4 Drawing WFS20 7AR...
Page 126: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 124 Wavefront Sensor 8 9 5 Drawing WFS20 7AR M...
Page 127: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 125 8 9 6 Drawing WFS20 14AR...
Page 128: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 126 Wavefront Sensor 8 9 7 Drawing WFS20 14AR M...
Page 129: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 127 8 9 8 Drawing WFS20 Control Box...
Page 130: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 128 Wavefront Sensor 8 9 9 Drawing WFS30 5C...
Page 131: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 129 8 9 10 Drawing WFS30 5C M...
Page 132: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 130 Wavefront Sensor 8 9 11 Drawing WFS30 7AR...
Page 133: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 131 8 9 12 Drawing WFS30 7AR M...
Page 134: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 132 Wavefront Sensor 8 9 13 Drawing WFS30 14AR...
Page 135: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 133 8 9 14 Drawing WFS30 14AR M...
Page 136: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 134 Wavefront Sensor 8 9 15 Drawing WFS40 5C...
Page 137: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 135 8 9 16 Drawing WFS40 5C M...
Page 138: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 136 Wavefront Sensor 8 9 17 Drawing WFS40 7AR...
Page 139: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 137 8 9 18 Drawing WFS40 7AR M...
Page 140: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 138 Wavefront Sensor 8 9 19 Drawing WFS40 14AR...
Page 141: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 139 8 9 20 Drawing WFS40 14AR M...
Page 144: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 142 Wavefront Sensor 8 11 Certifications and Compliances...
Page 145: ...2007 2018 Thorlabs 8 Appendix 143...
Page 153: ...www thorlabs com...