Saving and recalling information
Use these procedures to save or recall waveforms, setups, or traces.
The oscilloscope provides permanent storage for setups and waveforms. Use the internal storage of the oscilloscope to save setup files
and reference waveform data.
Use external storage, such as USB drives or network drives, to save setups, waveforms, and screen images. Use the external storage to
carry data to remote computers for further analysis and for archiving. USB drives must be FAT32 file systems.
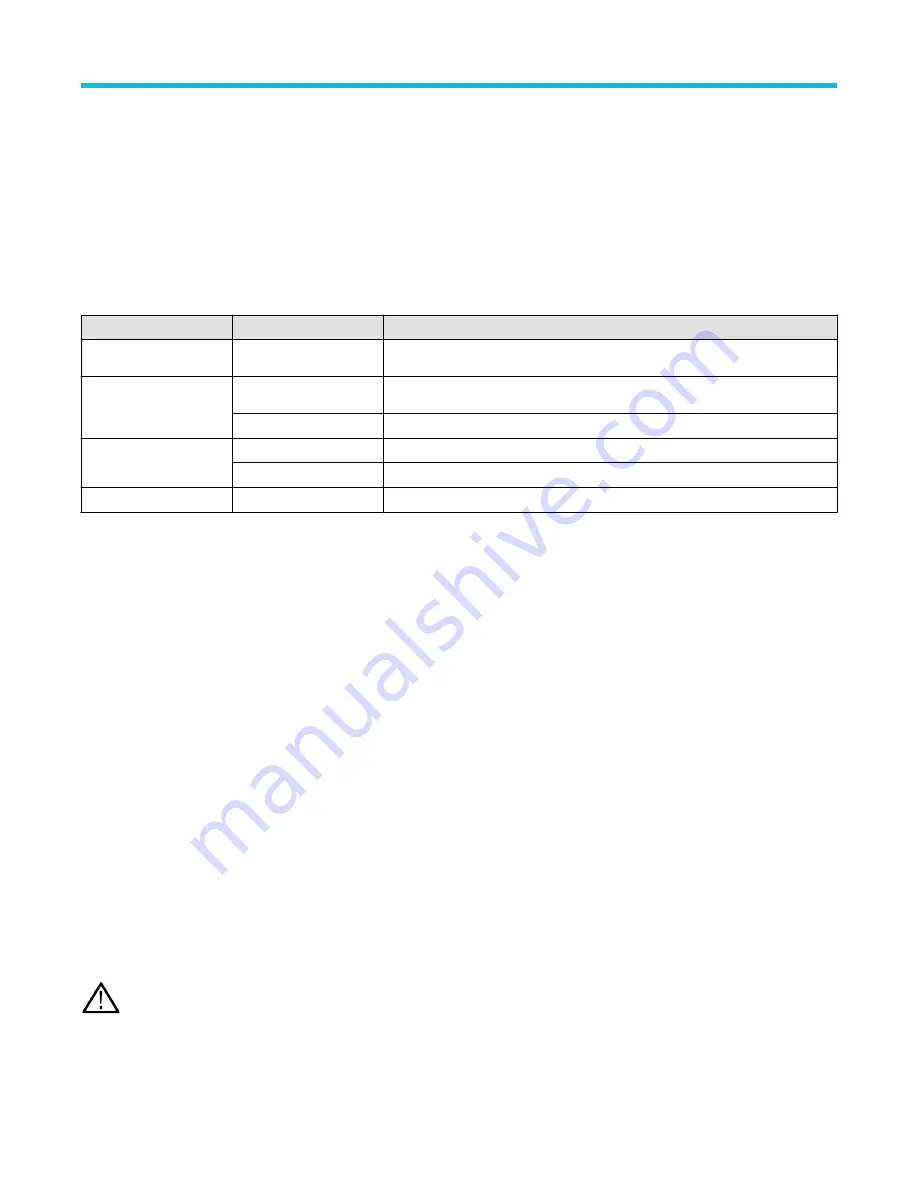
External file structure. If you are saving information to external storage, select the appropriate file.
Drive name
Drive letter
Drive or physical USB port location
Root drive
Instrument Storage
User-accessible memory on the oscilloscope
Front panel
E
USB 2.0 (top)
F
USB 2.0 (bottom)
Rear panel
G
USB 2.0
H
USB 2.0 device port provides USBTMC support
Network location
I through Z
Network storage locations
Browse to select the file location. Tap the + buttons to navigate to and select a location at which to save the file.
Naming your file.
The oscilloscope gives all files it creates a default name in the following format:
tekXXXXX.set for setup files where XXXXX is an integer from 00000 to 99999
tekXXXXX.png, tekXXXXX.bmp, or tekXXXXX.tif for image files
tekXXXXYYY.csv for spreadsheet files or tekXXXXYYY.isf for internal format files
For waveforms, the XXXX is an integer from 0000 to 9999. The YYY is the channel of the waveform, and can be one of the following:
CH1, CH2, CH3, or CH4 for the analog channels
D00, D01, D02, D03, and so on through D15 for the digital channels
MTH for a math waveform
RF1, RF2, RF3, or RF4 for reference memory waveforms
For RF traces, XXXX is an integer from 0000 to 9999. The YYY defines the trace and can be one of the following:
NRM for a normal trace
AVG for an average trace
MAX for a maximum hold trace
MIN for a minimum hold trace
TIQ for a baseband I & Q file
Note: Analog, digital, and RF waveforms and traces and those waveforms and traces derived from them (such as math and
references) can be saved to an ISF file.
The XXXX value will automatically increment each time you save a file of the same type. For example, the first time you save a file, that file
is named tek00000. The next time you save the same type of file, the file will be named tek00001.
Saving and recalling information
3 Series Mixed Domain Oscilloscope Printable Help
96






























