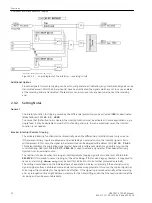
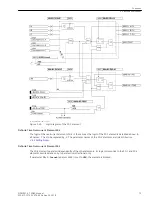
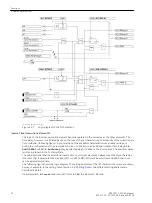
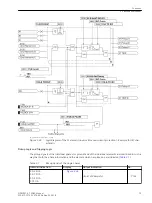
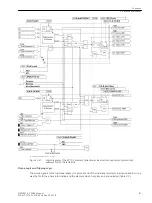
[lo-mitnahme-empfangskreis-20101108, 1, en_US]
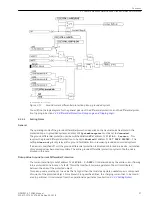
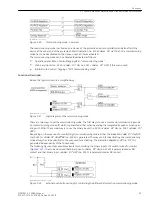
Figure 2-25
Logic diagram of the intertrip — receiving circuit
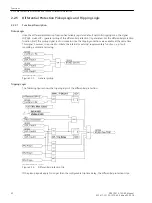
Additional Options
Since the signals for remote tripping can be set to just generate an indication, any other desired signals can be
transmitted as well. After the binary input(s) have been activated, the signals which are set to cause an alarm
at the receiving end are transmitted. These alarms can in turn execute any desired actions at the receiving
end.
Setting Notes
General
The intertrip function for tripping caused by the differential protection can be activated (
YES
) or deactivated
(
NO
) at address 1301
85 DT: SEND
.
To ensure that the faulted line is cleared, the intertrip function must be activated. In some applications, e.g. a
single feed, it may be desirable to switch off the feeding end only. In such exceptional cases, the intertrip
function is not needed.
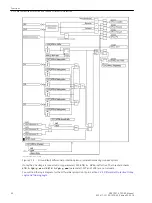
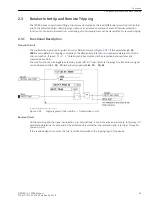
Breaker Intertrip / Remote Tripping
The activated intertrip function starts automatically when the differential protection trips at only one end.
If the relevant binary inputs are allocated and activated by an external source, the intertrip signal is trans-
mitted as well. In this case, the signal to be transmitted can be delayed with address 1303
85 DT: TD-BI
.
This delay stabilizes the originating signal against dynamic interferences which may possibly occur on the
control cabling. Address 1304
85 DT:T-PROL BI
is used to extend a signal after it has been effectively
injected from an external source.
The reaction of a device when receiving an intertrip/remote tripping signal is set in address 1302
85 DT:
RECEIVE
. If it is desired to cause tripping, set the value
Trip
. If the received signal, however, is supposed to
cause an alarm only,
Alarm only
must be set if this indication is to be further processed externally.
The setting times depend on the individual case of application. A delay is necessary if the external control
signal originates from a disturbed source and a restraint seems appropriate. Of course, the control signal has
to be longer than the delay for the signal to be effective. If the signal is processed externally at the receiving
end, a prolongation time might become necessary for the transmitting end so that the reaction desired at the
receiving end can be executed reliably.
2.3.2
Functions
2.3 Breaker Intertrip and Remote Tripping
70
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
Summary of Contents for SIPROTEC 4 7SD80
Page 8: ...8 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 10: ...10 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 18: ...18 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 248: ...248 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 298: ...298 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 312: ...312 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 322: ...322 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 400: ...400 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 402: ...402 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...