Communication
2.3 Modbus communication
SIMOCODE pro - Communication
96
Function Manual, 11/2018, A5E40508495002A/RS-AC/003
2.3.1.4
Modbus RTU data transfer
Principle of Modbus RTU data transfer
In contrast to cyclic/acyclic data transfer in the PROFIBUS bus system, the data are
transferred linearly using the Modbus protocol.
The master is an automation system (PLC). The slave is a SIMOCODE pro device.
The master takes the initiative in the data transfer. SIMOCODE pro works as a slave and
supplies the corresponding feedback signals to the bits/registers called up by the master, or
it accepts the bits/registers written by the master into the internal SIMOCODE memory.
The master sends requests to one or more slaves. The slave processes the requests of the
master and responds within a certain time with an acknowledgment, or with the requested
data, or an error code if applicable. The requests contain the function code and additional
data. The data can only be transferred between the master and a slave. Requests cannot be
transferred between slaves. A slave cannot transfer any information, e.g. alarms,
autonomously to the master. This always requires continuous polling of the corresponding bit
by the master.
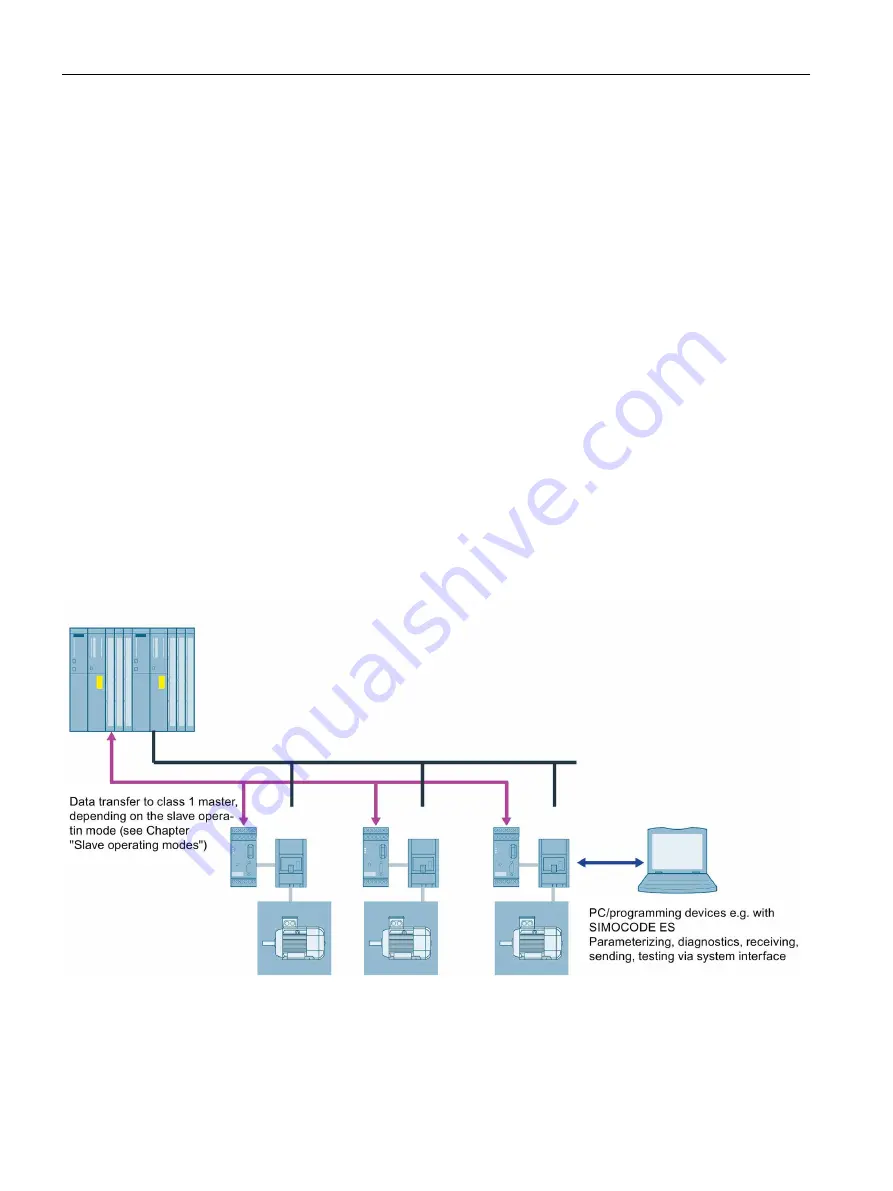
Data transfer options with Modbus RTU
The following figure shows the data transfer options:
Figure 2-30 Options for data transfer
















































