Configuring
S7-300 Programmable Controller Hardware and Installation
A5E00105492-01
4-31
On the PG you can specify individual MPI/PROFIBUS addresses for each one of
the nodes (on some of the PROFIBUS-DP slaves this is also possible per selector
switch).
Default MPI/PROFIBUS-DP addresses
The table below shows you the factory setting of the MPI/PROFIBUS-DP
addresses and the highest default MPI/PROFIBUS-DP addresses for the devices.
Table 4-12
MPI/PROFIBUS-DP addresses
Node
(device)
Default
MPI/PROFIBUS-
DP address
Default highest MPI
address
Default highest
PROFIBUS-DP address
PG
0
32
126
OP
1
32
126
CPU
2
32
126
Rules: Assigning MPI/PROFIBUS-DP addresses
Note the following rules before assigning MPI/PROFIBUS addresses:
•
All MPI/PROFIBUS addresses in a subnet must be unique.
•
The highest MPI/PROFIBUS address must be
≥
of the physical
MPI/PROFIBUS address, and it must be identical for each node. (Exception:
Connecting a PG to multiple nodes; refer to the next Chapter).
Differences in the case of MPI addresses of CPs/FMs in an S7-300
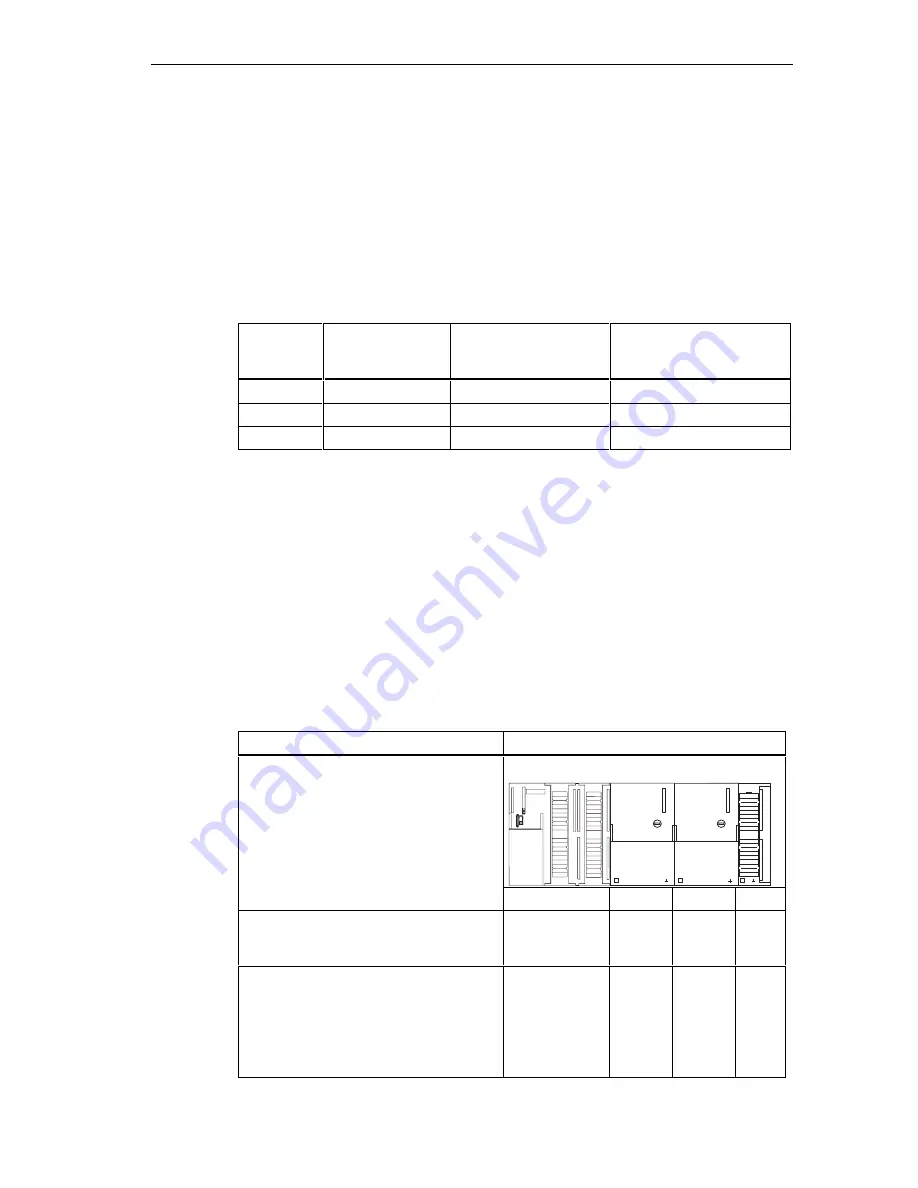
Table 4-13
MPI addresses of CPs/FMs in an S7-300
Options
Example:
CPU
CP
SF
BUSF
DC5V
FRCE
RUN
STOP
CP
Example:
An S7-300 CPU and 2 CPs in one unit.
You have two options for assigning MPI
addresses of CPs/FMs installed in one
unit:
CPU
CP
CP
First option: The CPU adopts the CP
MPI addresses you specify in STEP 7.
MPI address
MPI
address
+x
MPI
address.
+y
Second option: The CPU automatically
determines the CP MPI addresses in your
configuration according to the following
pattern: MPI address CPU; MPI address
+1; MPI a2.
(Default)
MPI address
MPI
address
+1
MPI
address
+2
Summary of Contents for Simatic S7-300
Page 10: ...Contents S7 300 Programmable Controller Hardware and Installation x A5E00105492 01 ...
Page 16: ...Preface S7 300 Programmable Controller Hardware and Installation 1 6 A5E00105492 01 ...
Page 22: ...Quick Guide S7 300 Programmable Controller Hardware and Installation 2 6 A5E00105492 01 ...
Page 28: ...Product overview S7 300 Programmable Controller Hardware and Installation 3 6 A5E00105492 01 ...
Page 74: ...Configuring S7 300 Programmable Controller Hardware and Installation 4 46 A5E00105492 01 ...
Page 102: ...Wiring S7 300 Programmable Controller Hardware and Installation 6 18 A5E00105492 01 ...
Page 148: ...Commissioning S7 300 Programmable Controller Hardware and Installation 8 36 A5E00105492 01 ...
Page 236: ...Glossary S7 300 Programmable Controller Hardware and Installation 12 16 A5E00105492 01 ...






























