S5-115U Manual
Communications Capabilities
12
Communications Capabilities
The processors of individual modules (CPUs, CPs, or intelligent I/Os) can exchange information in
different ways.
12.1
Data Interchange
There are three ways of organizing data interchange between the S5-115U CPUs and CPs/IPs:
•
Data interchange over interprocessor communication flags (e.g. in the case of CP 525 and
CP 526)
•
Data interchange over dual-port RAM (page addressing)
•
Data interchange over the I/O area (e.g. CP 523; PROFIBUS with global and cyclic I/O)
Interprocessor communication flags and page addressing are described in the following sub-
sections; see the "SINEC L2 Local Area Network" Manual for more detailed information on data
interchange over the I/O area using PROFIBUS.
12.1.1 Interprocessor Communication Flags
Binary signals are exchanged between central processing units (CPU 941 to CPU 944) and some
communications processors, e.g., CP 526, via interprocessor communication flags. The CPU pro-
cesses interprocessor communication flags like normal flags. However, they are stored in a special
256-byte memory area between the addresses F200
H
and F2FF
H
.
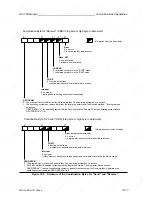
The control program must identify interprocessor communication flags byte by byte in data block
DB1 as input flags or output flags.
The transfer of interprocessor communication flags is similar to the transfer of inputs and outputs
to and from the process images. The procedure is as follows:
•
The interprocessor communication input flags are read in and stored in the appropriate
memory area prior to program scanning.
•
Interprocessor communication output flags are transferred to the appropriate CPs at the end
of program scanning.
Interprocessor communication output flags can be treated like normal flags.
Interprocessor communication input flags should be scanned only, since the setting or resetting of
bits can be canceled during the next data transfer.
Definition of the Interprocessor Communication Flags in DB1
You can program DB1 in the following two ways:
•
with the help of a screen form on a programmer
•
through direct input of data words
EWA 4NEB 811 6130-02b
12-1
Summary of Contents for SIMATIC S5-115U
Page 6: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 16: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 18: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 26: ......
Page 62: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 64: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 67: ......
Page 74: ......
Page 79: ......
Page 80: ......
Page 81: ......
Page 82: ......
Page 83: ......
Page 84: ......
Page 97: ......
Page 98: ......
Page 99: ......
Page 114: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 280: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 372: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 432: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 442: ......
Page 528: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 590: ......
Page 591: ......
Page 592: ......
Page 593: ......
Page 594: ......
Page 600: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 602: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 604: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 624: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 632: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 644: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 646: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 652: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 654: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 660: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 662: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 666: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 668: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...
Page 674: ...EWA 4NEB 811 6130 02b ...