Chapter 5
Setup and Configuration
RUGGEDCOM ROX II
User Guide
382
Configuring a Broadcast Address
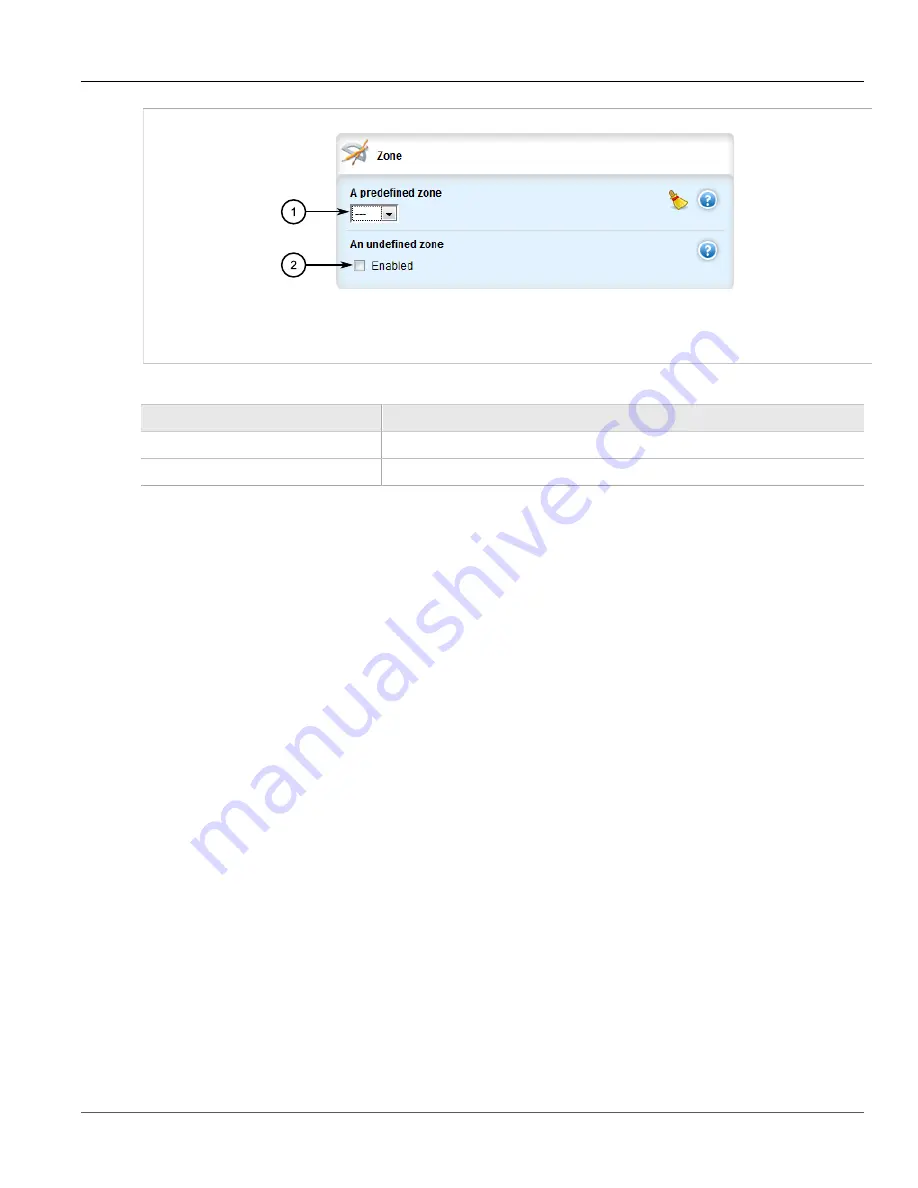
Figure 416: Zone Form
1.
Predefined Zone List
2.
Undefined Zone Check Box
3. Configure the following parameter(s) as required:
Parameter
Description
predefined-zone
A pre-defined zone
undefined-zone
This is used in conjunction with hosts definitions.
4. Click
Commit
to save the changes or click
Revert All
to abort. A confirmation dialog box appears. Click
OK
to proceed.
5. Click
Exit Transaction
or continue making changes.
Section 5.17.9.4
Configuring a Broadcast Address
To configure a broadcast address for an interface, do the following:
1. Change the mode to
Edit Private
or
Edit Exclusive
.
2. Navigate to
security
»
firewall
»
fwconfig
»
fwconfig
»
{firewall}
»
fwinterface{interface}
»
broadcast-
addr
, where
{firewall}
is the name of the firewall and
{interface}
is the name of the interface. The
Broadcast
Address
form appears.
Summary of Contents for RUGGEDCOM RX1510
Page 32: ...RUGGEDCOM ROX II User Guide Preface Customer Support xxxii ...
Page 44: ...RUGGEDCOM ROX II User Guide Chapter 1 Introduction User Permissions 12 ...
Page 62: ...RUGGEDCOM ROX II User Guide Chapter 2 Using ROX II Using the Command Line Interface 30 ...
Page 268: ...RUGGEDCOM ROX II User Guide Chapter 4 System Administration Deleting a Scheduled Job 236 ...






























