Semiconductor Group
2-2
1997-10-01
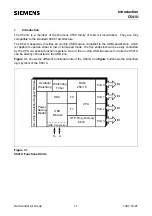
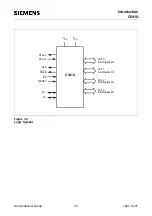
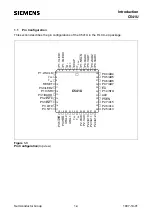
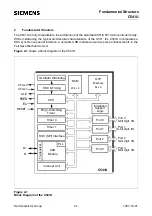
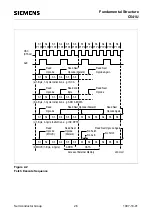
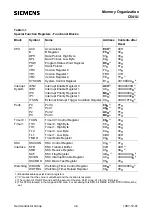
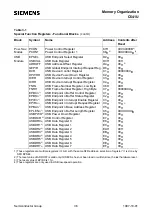
Fundamental Structure
C541U
2.1
CPU
The CPU is designed to operate on bits and bytes. The instructions, which consist of up to 3 bytes,
are performed in one, two or four machine cycles. One machine cycle requires six oscillator cycles
(this number of oscillator cycles differs from other members of the C500 microcontroller family). The
instruction set has extensive facilities for data transfer, logic and arithmetic instructions. The
Boolean processor has its own full-featured and bit-based instructions within the instruction set. The
C541U uses five addressing modes: direct access, immediate, register, register indirect access,
and for accessing the external data or program memory portions a base register plus index-register
indirect addressing. Efficient use of program memory results from an instruction set consisting of
44% one-byte, 41% two-byte, and 15% three-byte instructions. With a 12 MHz clock, 58% of the
instructions execute in 500 ns.
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) of the C541U consists of the instruction decoder, the arithmetic
section and the program control section. Each program instruction is decoded by the instruction
decoder. This unit generates the internal signals controlling the functions of the individual units
within the CPU. They have an effect on the source and destination of data transfers and control the
ALU processing.
The arithmetic section of the processor performs extensive data manipulation and is comprised of
the arithmetic/logic unit (ALU), an A register, B register and PSW register.
The ALU accepts 8-bit data words from one or two sources and generates an 8-bit result under the
control of the instruction decoder. The ALU performs the arithmetic operations add, substract,
multiply, divide, increment, decrement, BDC-decimal-add-adjust and compare, and the logic
operations AND, OR, Exclusive OR, complement and rotate (right, left or swap nibble (left four)).
Also included is a Boolean processor performing the bit operations as set, clear, complement, jump-
if-not-set, jump-if-set-and-clear and move to/from carry. Between any addressable bit (or its
complement) and the carry flag, it can perform the bit operations of logical AND or logical OR with
the result returned to the carry flag.
The program control section controls the sequence in which the instructions stored in program
memory are executed. The 16-bit program counter (PC) holds the address of the next instruction to
be executed. The conditional branch logic enables internal and external events to the processor to
cause a change in the program execution sequence.
Accumulator
ACC is the symbol for the accumulator register. The mnemonics for accumulator-specific
instructions, however, refer to the accumulator simply as A.
Program Status Word
The Program Status Word (PSW) contains several status bits that reflect the current state of the
CPU.
Summary of Contents for C541U
Page 1: ... 8 LW 026 0LFURFRQWUROOHU 8VHU V 0DQXDO http www siem ens d Sem iconductor ...
Page 7: ......
Page 21: ...Semiconductor Group 2 6 1997 10 01 Fundamental Structure C541U ...
Page 37: ...Semiconductor Group 4 6 1997 10 01 External Bus Interface C541U ...
Page 133: ...Semiconductor Group 6 88 1999 04 01 On Chip Peripheral Components C541U ...
Page 163: ...Semiconductor Group 8 8 1997 10 01 Fail Safe Mechanisms C541U ...
Page 185: ...Semiconductor Group 10 14 1997 10 01 OTP Memory Operation C541U ...