30
02.00|0889073_ROTA TB-TBS-EP |en
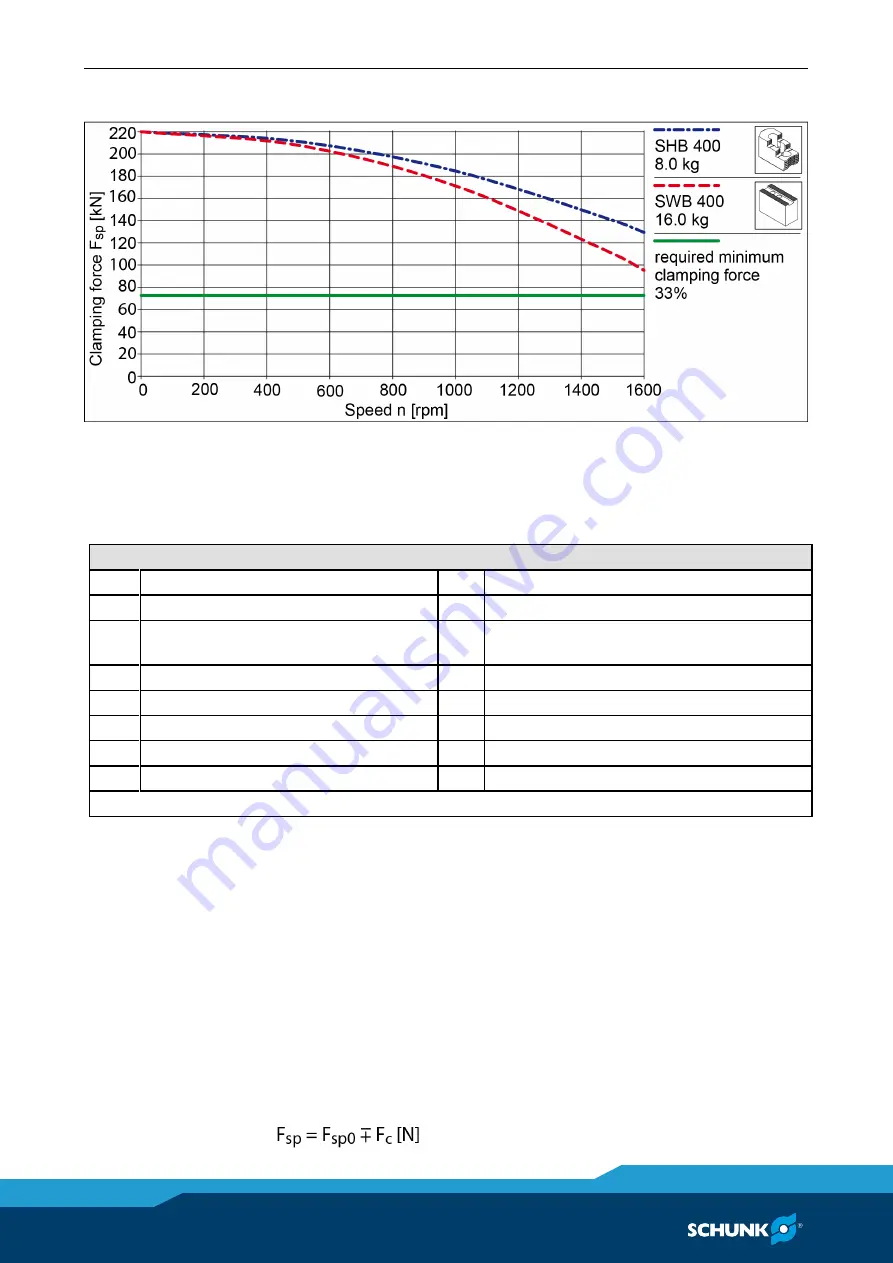
Clamping force-RPM-diagram ROTA EP-LH 460-185
Calculations for clamping force and speed
Missing information or specifications can be requested from the
manufacturer.
Legend
F
c
Total centrifugal force [N]
M
cAB
Centrifugal torque of top jaws [Kgm]
F
sp
Effective clamping force [N]
M
cGB
Centrifugal torque of base jaws [Kgm]
F
spmin
minimum required clamping force
[N]
n
Speed of rotation [RPM]
F
sp0
Initial clamping force [N]
r
s
Center of gravity radius [mm]
F
spz
Cutting force [N]
r
sAB
Center of gravity radius of top jaw [mm]
m
AB
Mass of one top jaw [kg]
s
sp
Safety factor for clamping force
m
B
Mass of chuck jaw set [kg]
s
z
Safety factor for machining
M
c
Centrifugal torque [kgm]
Σ
s
Max. clamping force of lathe chuck [N]
kgm × 9.81 = Nm
Calculation of the required clamping force in case of a given rpm
The
initial clamping force F
sp0
is the total force impacting radially
on the workpiece via the jaws due to actuation of the lathe chuck
during shutdown. Under the influence of rotation, the jaw mass
generates an additional centrifugal force. The centrifugal force
reduces or increases the initial clamping force depending on
whether gripping is from the outside inwards or from the inside
outwards.
The sum of the initial clamping force
F
sp0
and the
total centrifugal
force F
c
is
the effective clamping force F
sp
.
6.3
6.3.1
Summary of Contents for ROTA EP 380-127
Page 64: ...Assembly drawings 64 02 00 0889073_ROTA TB TBS EP en Assembly drawings TB 400 850 16 ...
Page 66: ...Assembly drawings 66 02 00 0889073_ROTA TB TBS EP en TB 400 850 LH ...
Page 67: ...Assembly drawings 02 00 0889073_ROTA TB TBS EP en 67 X Clamping stroke TB 1000 LH ...
Page 68: ...Assembly drawings 68 02 00 0889073_ROTA TB TBS EP en ...
Page 69: ...Assembly drawings 02 00 0889073_ROTA TB TBS EP en 69 EP LH ...
Page 70: ...Assembly drawings 70 02 00 0889073_ROTA TB TBS EP en ...






























