Installation manual
PSC1-C-10 Installation manual V2.6
Page 154 of 173
Version: 57E
12.3.3
Specification of the functional safety system
Derived from the general hazard and risk analysis for the machine, the active protection functions are
to be identified and specified.
Active protection functions are, e.g. safely limited speed in certain system states, monitored stop and
standstill functions, range monitoring, processing of monitoring devices such as light grids, safety mats
etc.
The safety functions are each to be bounded and the specific requirements defined in relation to
function and safety level.
12.3.3.1
Definition of the safety functions
The definition of the safety function must:
State the risk to be covered
Describe the exact function
List all sensors, controls involved
Identify all controllers
Identify the related shutdown circuit.
The definition is intended to form the basis for the specification of the hardware and software design.
For each of the safety functions defined in this manner, any parameters to be used, e.g. max. system
speed in the setting up mode etc. are to be defined.
Example for safety functions:
SF1: STO (safe torque off) for protection against safe startup
SF2: Safe speeds
SF3: Safe positions
SF4.:……
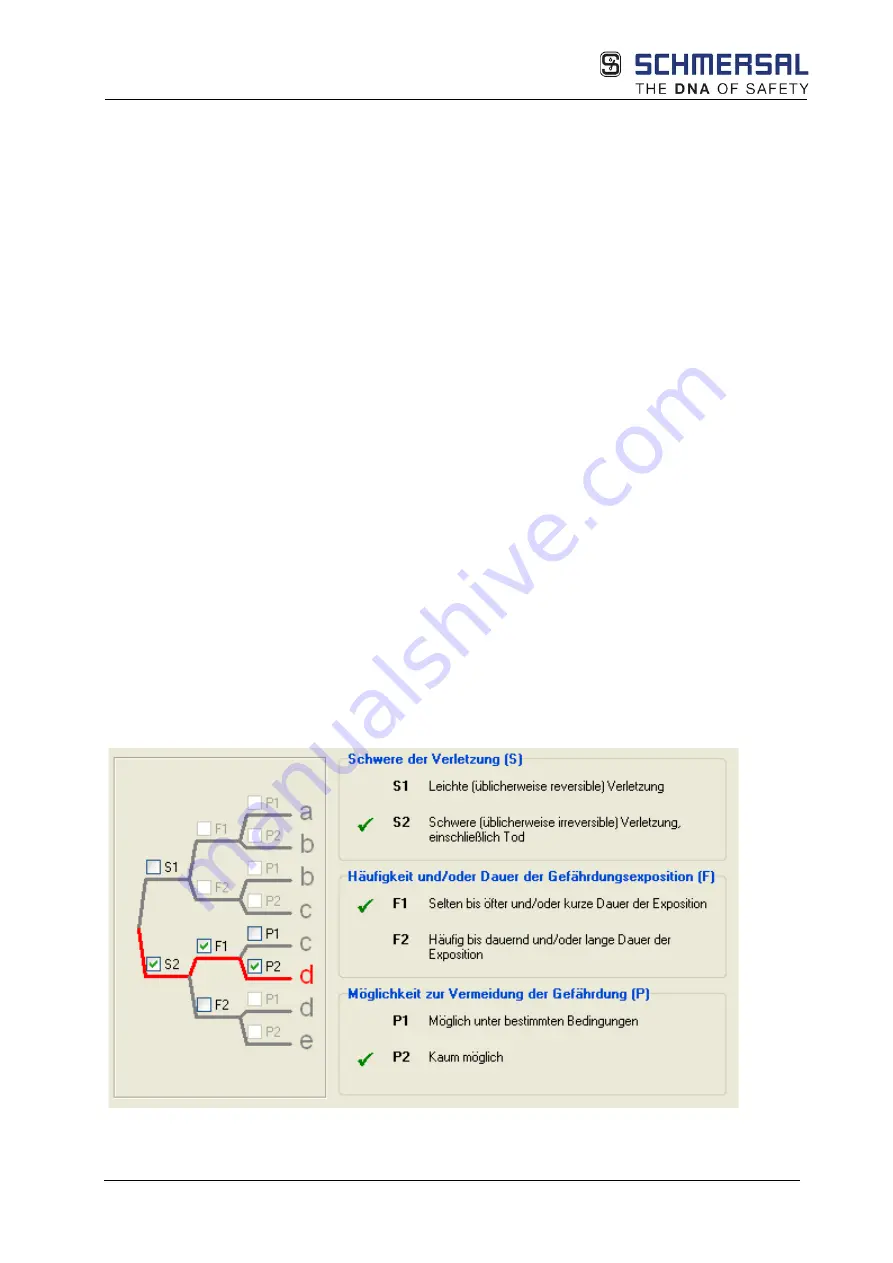
12.3.3.2
Performance Level required (PLr) (additional emergency stop)
The Performance Level
required must now be determined from the safety functions SF1….. stated
above. The decision path can be seen in the example below.
Example for SF1: Result PF = d (source Sistema)






























