8
Operating instructions
Solenoid interlock
AZM 200
EN
9. Appendix
9.1 Wiring examples
The application examples shown are suggestions. They however do not release the user from carefully checking whether the switchgear and its
set-up are suitable for the individual application.
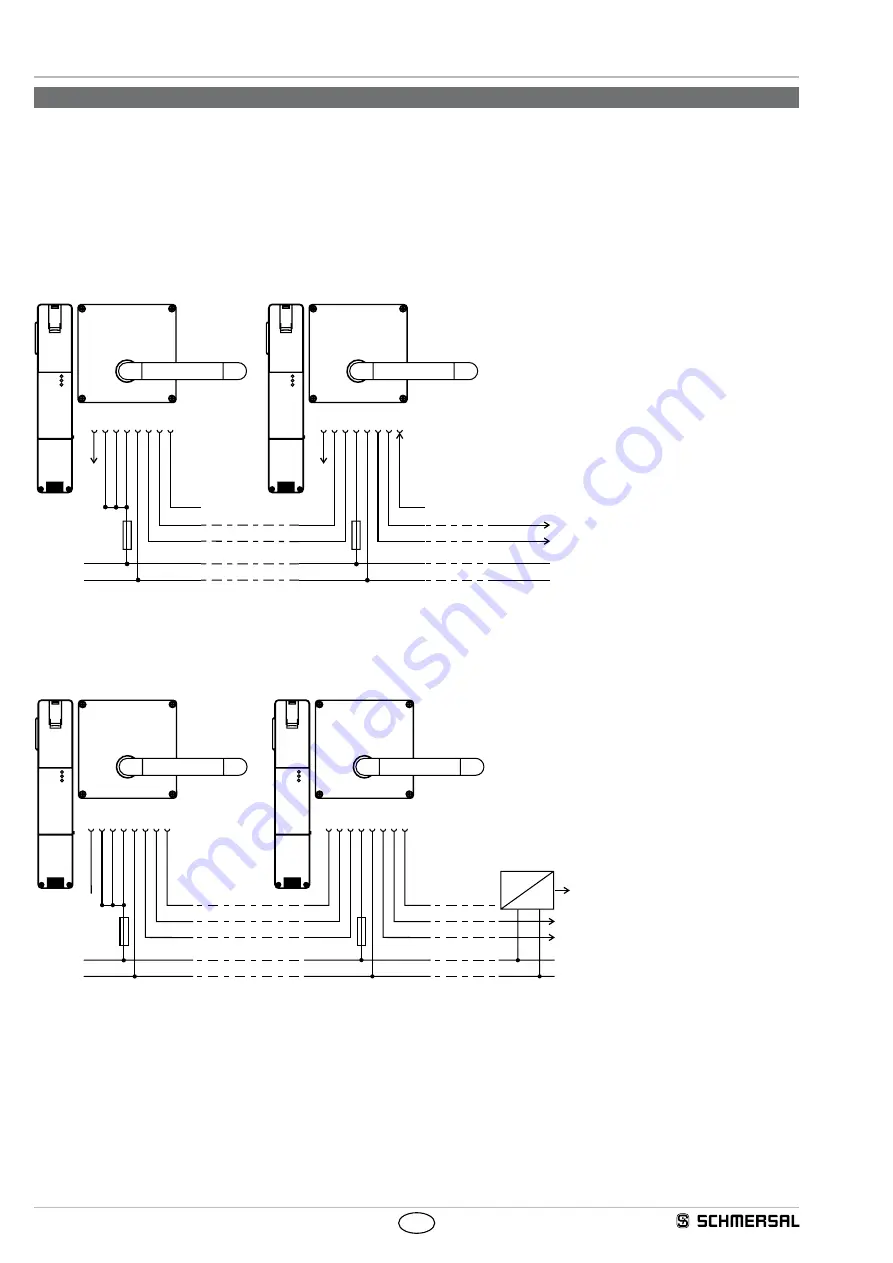
Wiring example 1: Series-wiring of the AZM 200 with conventional diagnostic output
The series-wiring of multiple AZM 200 solenoid interlocks is realised by wiring in the control cabinet or in on-site junction boxes.
In the example, 2 AZM 200 solenoid interlocks (max. 31 components) are wired in series. The diagnostic output ("OUT") and the magnet control
("IN") are separately wired to a conventional PLC for evaluation or control. The maximum cable length of the safety circuits must not exceed 200 m.
In the series-wiring, the 24V-X1-X2 bridge must be removed from all components up to the last component.
The voltage is supplied at both safety inputs of the terminal safety component of the chain (considered from the safety-monitoring module).
The safety outputs of the first safety component are wired to the safety-monitoring module.
X1
Y1
X2
Y2
1
2
3
5
6
8
X1 X2 24V GND
Y1
Y2
1
2
3
5
6
8
X1
4
Y1
4
Y1
X2
7
Y2
7
Y2
OUT
24V GND
OUT
SPS/PLC
IN
SPS/PLC
SPS/PLC
IN
24 VDC
GND
SPS/PLC
n-participants max. 31 components in series
Safety outputs
evaluation
Wiring example 2: Series-wiring of the AZM 200 with serial diagnostic function
The safety outputs of the first safety component are wired to the safety-monitoring module. The serial Diagnostic Gateway is connected to the serial
diagnostic input of the first safety component.
n-participants max. 31 components in series
Safety outputs
evaluation
Field bus
24 VDC
GND
1
2
3
5
4
6
8
X1
Y1
X2
SD IN
SD OUT
1
2
3
5
4
6
8
X1
Y1
X2
7
Y2
7
Y2
SD IN
SD OUT
X1
Y1
X2
Y2
SD IN
SD OUT
Y1
Y2
SD IN
24V GND
24V GND










