135
has exceeded 3
ˊ
at this time and exceeds the designated compensation range.
4. Rotate the above screw to its original position, and the instrument display
screen will show the vertical angle again, meaning that the vertical index
difference compensation function is working.
Adjust
If the compensation function is not working, send the instrument back to the
factory for repair.
10.6 VERTICAL INDEX DIFFERENCE (I ANGLE) & SETTING VERTICAL INDEX 0
Before inspecting this session, check and adjust the Session 10.3 and 10.5.
Check
1. Power on after leveling the instrument. Collimate object A in Face I and read
the Vertical angle value L.
2. Rotate the telescope. Sight object B in Face
Ⅱ
and read the Vertical angle
value R.
3. If the vertical angle is 0°in zenith, i=(L+R-360°)/2
If the vertical angle is 0° in horizon. i=(L+R-180°)/2 or (L+R-540°)/2.
4. If
|
i
|
≥10″, you should set the Vertical Angle 0 Datum again.
Adjust
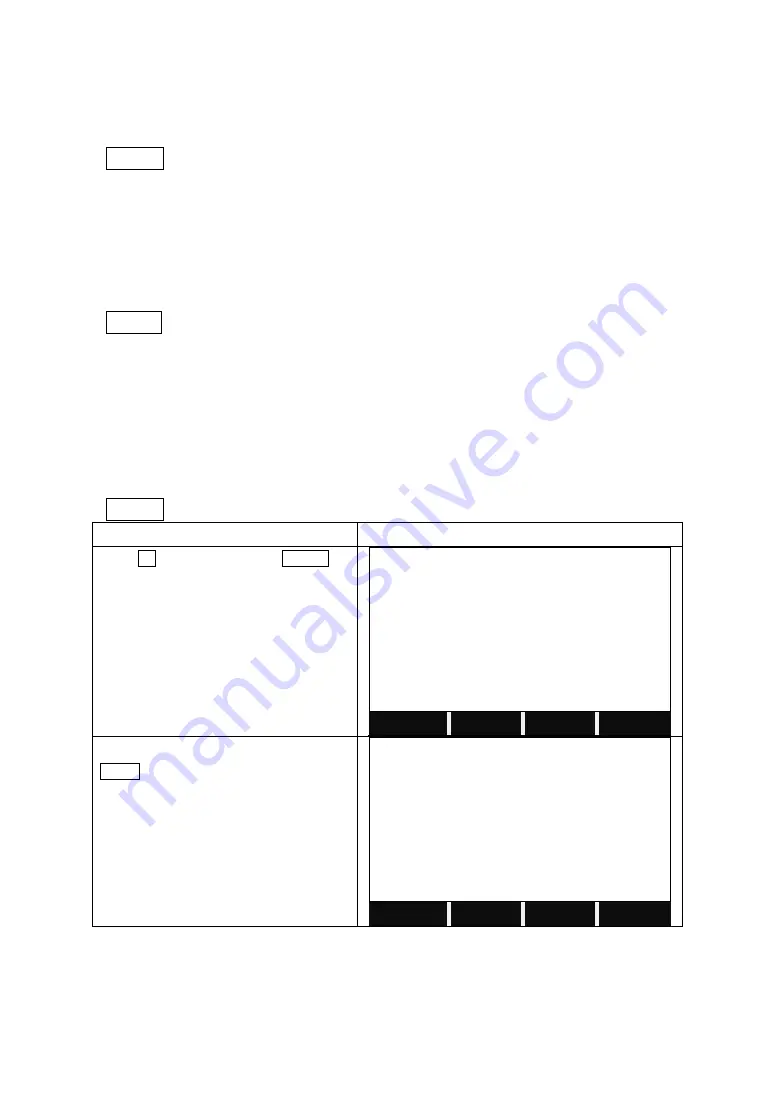
STEPS
DISPLAY
Press F1 to start to adjust the V-index.
【
Adjustment
】
▼
F1 V-index
(1)
F2 Hz-collimation
(2)
F3 Horizontal Axis
(3)
F4 V0/Axis (Cons. List)
(4)
F1
F2
F3
F4
In Face I, collimate the target, and press
MEAS.
【
V-index
】
<STEP-1> Front
Hz
:
335°28’41”
V
:
107°16’20”
Sight target
MEAS
Summary of Contents for STS-750RC Series
Page 1: ......
Page 12: ...11 1 8 MENU TREE Menu F1 F4 Confirms the selected menu Press PAGE to view the next page ...
Page 152: ......
















































