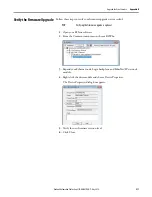
Rockwell Automation Publication 2198-UM001D-EN-P - May 2014
225
Induction Motor Support
Appendix D
Sensorless Vector
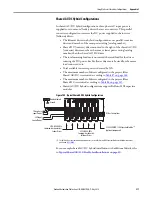
Sensorless Vector mode uses a volts/hertz core enhanced by a current resolver, slip
estimator, and a voltage boost compensator based on the operating conditions of
the motor.
Figure 108 - Sensorless Vector Method
The algorithms operate on the knowledge of the relationship between the rated
slip and torque of the motor. Drive uses applied voltages and measured currents
to estimate operating slip frequency. You can enter values to identify the motor
resistance value or you can run an autotune routine to identify the motor
resistance value (see
). This is done so that the drive
can accurately estimate the required boost voltage.
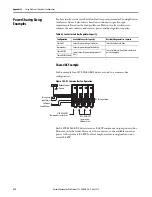
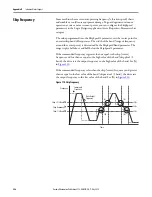
This method offers better torque production and speed regulation over a wider
speed range than basic volts/hertz. However, it is not appropriate when more
than one motor is connected to the same drive.
The auto boost feature is applied internally to compensate voltage drop and
improve starting torque.
Figure 109 - Approximate Load Curve
+
x
+
Velocity Trim
Velocity Command
Slip Speed
V/Hz
Motor Pole
Pairs
Vboost
Estimator
Voltage
Control
Current
Feedback
Current
Resolver
Torque
Estimate
Load
Torque
Estimator
Slip
Estimation
Inverter
Motor
Frequency,
max
Ideal, volts/hertz
Base Frequency,
(nameplate)
Dynamic
Boost Applied
Base Voltage
(nameplate)
Voltage, max
Auto Boost