Getting Started
R&S
®
FSPN
56
User Manual 1179.4363.02 ─ 01
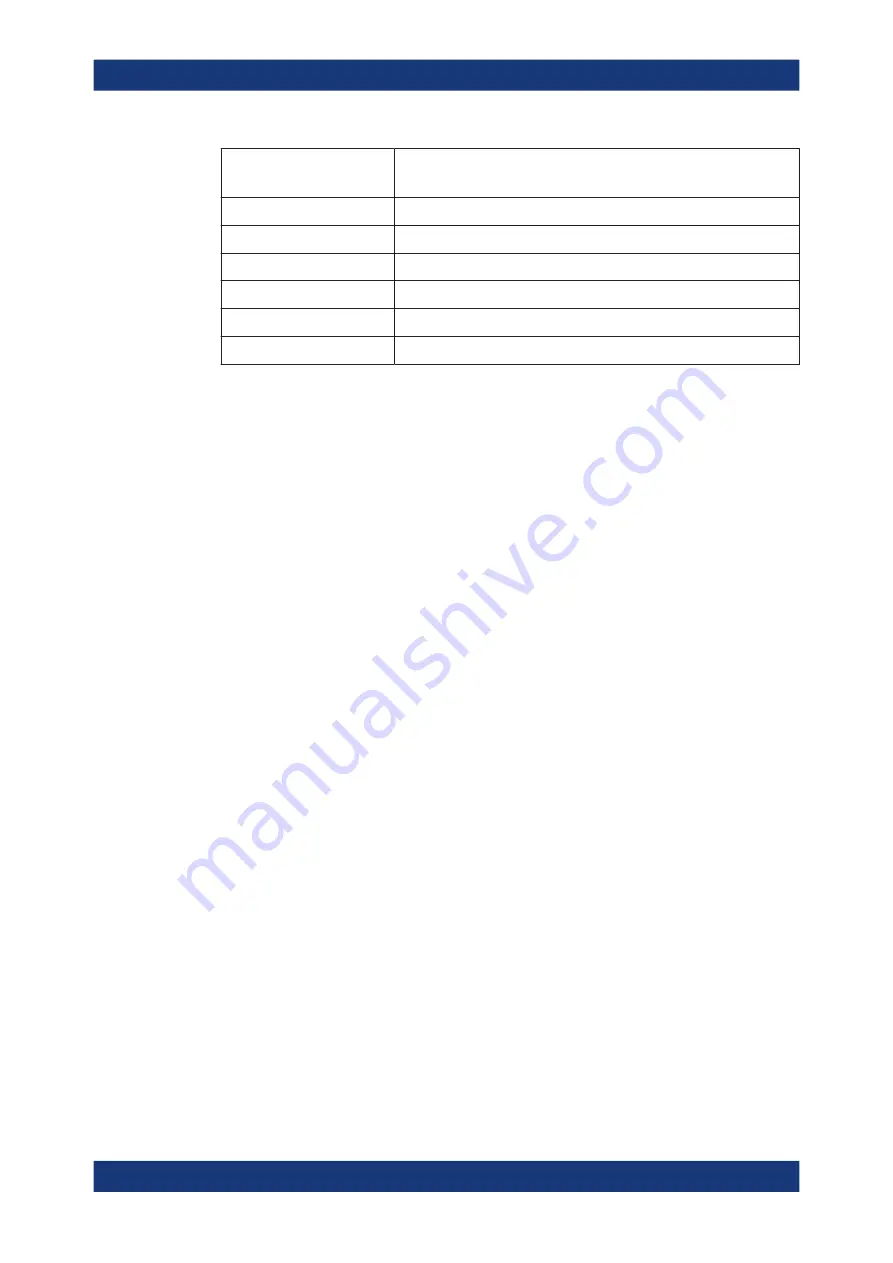
Key name
(upper inscription)
Series of (special) characters and number provided
1
P Q R S 1
2
T U V 2 Ü
3
W X Y Z 3
0
<blank> 0 – @ + / \ < > = % &
.
. * : _ , ; " ' ? ( ) #
–
<toggles between capital and small letters>
3.3.5
Displaying Results
The results of a measurement channel can be evaluated in many different ways, both
graphically and numerically. For each evaluation method the results are displayed in a
separate window in the tab.
The R&S
FSPN allows you to configure the display to suit your specific requirements
and optimize analysis.
3.3.5.1
Activating and Deactivating Channels
When you activate an application, a new measurement channel is created which deter-
mines the measurement settings for that application. The same application can be acti-
vated with different measurement settings by creating several channels for the same
application. Whenever you switch channels, the corresponding measurement settings
are restored. Each channel is displayed in a separate tab on the screen.
An additional tab ("MultiView") provides an overview of all currently active channels at
once.
Only one measurement can be performed at any time, namely the one in the currently
active channel. However, in order to perform the configured measurements consecu-
tively, a Sequencer function is provided.
Operating the Instrument






























