GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Series Hardware Design
MC60_Series_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 37 / 114
3.6.2. Operating Modes of GNSS Part
3.6.2.1. Full on Mode
Full on mode includes tracking mode and acquisition mode. Acquisition mode is defined as that the GNSS
part starts to search satellites, and to determine the visible satellites, coarse carrier frequency & code
phase of satellite signals. When the acquisition is completed, it switches to tracking mode automatically.
Tracking mode is defined as that the GNSS part tracks satellites and demodulates the navigation data
from specific satellites.
When the GNSS_VCC is valid, the GNSS part will enter into full on mode automatically. The following
table describes the default configuration of full on mode.
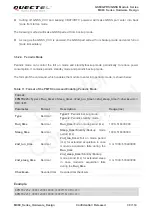
Table 10: Default Configuration of Full on Mode (GNSS part)
Item
Configuration
Comment
Baud Rate
115200bps
Protocol
NMEA
RMC, VTG, GGA, GSA, GSV and GLL
Update Rate
1Hz
SBAS
Enable
AIC
Enable
LOCUS
Disable
EASY Technology
Enable
EASY will be disabled automatically when update
rate exceeds 1Hz.
GNSS
GPS+GLONASS
In full on mode, the consumption complies with the following regulations:
When the GNSS part is powered on, the average current will rush to 40mA and last for a few seconds;
then the consumption will be decreased to the acquisition current marked in
Table 3
and Quectel defined
this state as acquisition state, and also it will last for several minutes until it switches to tracking state
automatically. The consumption in tracking state is less than that in acquisition state. The value is also
listed in
Table 3
.
Sending PMTK commands allows for switching among multiple positioning systems:
$PMTK353,0,1,0,0,0*2A: search GLONASS satellites only
Quectel
Confidential