17–QLogic Teaming Services
Teaming Mechanisms
288
83840-546-00 D
Outbound Traffic Flow
The QLogic Intermediate Driver manages the outbound traffic flow for all teaming
modes. For outbound traffic, every packet is first classified into a flow, and then
distributed to the selected physical adapter for transmission. The flow
classification involves an efficient hash computation over known protocol fields.
The resulting hash value is used to index into an Outbound Flow Hash Table.The
selected Outbound Flow Hash Entry contains the index of the selected physical
adapter responsible for transmitting this flow. The source MAC address of the
packets will then be modified to the MAC address of the selected physical
adapter. The modified packet is then passed to the selected physical adapter for
transmission.
The outbound TCP and UDP packets are classified using Layer 3 and Layer 4
header information. This scheme improves the load distributions for popular
Internet protocol services using well-known ports such as HTTP and FTP.
Therefore, ASP performs load balancing on a TCP session basis and not on a
packet-by-packet basis.
In the Outbound Flow Hash Entries, statistics counters are also updated after
classification. The load-balancing engine uses these counters to periodically
distribute the flows across teamed ports. The outbound code path has been
designed to achieve best possible concurrency where multiple concurrent
accesses to the Outbound Flow Hash Table are allowed.
For protocols other than TCP/IP, the first physical adapter will always be selected
for outbound packets. The exception is Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which
is handled differently to achieve inbound load balancing.
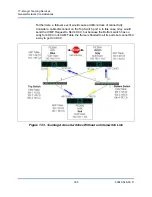
Inbound Traffic Flow (SLB Only)
The QLogic intermediate driver manages the inbound traffic flow for the SLB
teaming mode. Unlike outbound load balancing, inbound load balancing can only
be applied to IP addresses that are located in the same subnet as the
load-balancing server. Inbound load balancing exploits a unique characteristic of
Address Resolution Protocol (RFC0826), in which each IP host uses its own ARP
cache to encapsulate the IP Datagram into an Ethernet frame. ASP carefully
manipulates the ARP response to direct each IP host to send the inbound IP
packet to the desired physical adapter. Therefore, inbound load balancing is a
plan-ahead scheme based on statistical history of the inbound flows. New
connections from a client to the server will always occur over the primary physical
adapter (because the ARP Reply generated by the operating system protocol
stack will always associate the logical IP address with the MAC address of the
primary physical adapter).
Like the outbound case, there is an Inbound Flow Head Hash Table. Each entry
inside this table has a singly linked list and each link (Inbound Flow Entries)
represents an IP host located in the same subnet.
Summary of Contents for 8400 Series
Page 390: ......