G.SHDSL .bis Router User Manual V0.04
34
Version
Select from:
RIP-V1
: Only sends RIP v1 messages only
RIP-V2
: Sends RIP v2 messages in multicast and broadcast format
Auth Type
Select from (1)Simple (2)MD5
Auth Code
Enter the Corresponded Authentication Code for the Type picked above
Split Horizon
Enable or Disable Split Horizon feature
Click Apply to save the parameters changed or Back to return to previous page
4
4
.
.
3
3
.
.
9
9
N
N
A
A
T
T
/
/
D
D
M
M
Z
Z
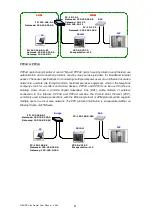
NAT
(Network Address Translation) is the translation of an Internet Protocol address (IP address)
used within one network to a different IP address known within another network. One network is
designated the inside network and the other is the outside. Typically, a company maps its local
inside network addresses to one or more global outside IP addresses and reverse the global IP
addresses of incoming packets back into local IP addresses. This ensure security since each
outgoing or incoming request must go through a translation process, that also offers the
opportunity to qualify or authenticate the request or match it to a previous request. NAT also
conserves on the number of global IP addresses that a company needs and lets the company to
use a single IP address of its communication in the Internet world.
DMZ
(Demilitarized zone) is a computer host or small network inserted as a “neutral zone”
between a company private network and the outside public network. It prevents outside users from
getting direct access to a server that has company private data.
In a typical DMZ configuration for an enterprise, a separate computer or host receives requests
from users within the private network to access via Web sites or other companies accessible on the
public network. The DMZ host then initiates sessions for these requests to the public network.
However, the DMZ host is not able to initiate a session back into the private network. It can only
forward packets that have already been requested.
Users of the public network outside the company can access only the DMZ host. The DMZ may
typically also have the company’s Web pages so these could serve the outside world. However, the
DMZ provides access to no other company data. In the event that an outside user penetrated the
DMZ host’s security, the Web pages might be corrupted, but no other company information would
be exposed.
ADVANCED>NAT/DMZ
NAT v.s DMZ Setup
Item
Description
NAT/DMZ Mode
Select to Enable or Disable NAT/DMZ mode