9928487 R01 - 2018 RANGER XP 1000 Service Manual
© Copyright Polaris Industries Inc.
11.43
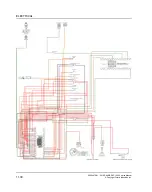
TESTING FOR A SHORT TO VOLTAGE
There are three possible short to voltage causes:
1. Internal electronic component short.
2. Harness chaffing leading to contact of the circuit
being diagnosed to one with B + or a different
reference voltage.
3. Moisture in a connector or component.
TESTING PROCEDURE
1. Consult the wiring diagram. Determine which circuit
you will be testing.
2. Ensure that any static voltage checks advised in
relation to the DTC or concern you are diagnosing
have been performed and are in spec.
3. Ensure you have checked continuity of the circuit.
Testing Continuity/Resistance, page 11.41
4. Ensure you have checked for a short to ground.
Testing For A Short To Ground, page 11.42
5. Ensure that neither end of the circuit is connected.
6. Set your DMM to DC volts.
7. Connect one meter lead securely to the battery
negative post.
8. Connect the other lead to either end of the
disconnected circuit. Ensure you are using the correct
adapter.Connector Probing Guidelines, page 11.40
9. If there is voltage present, the harness is damaged
and should be repaired or replaced. You may need to
remove the protective tape and tubing to inspect.
10. If the DMM reads 0 volts, the concern may be in a
component related to the circuit. If so, checking
internal continuity of non-electronic components may
reveal the concern, but diagnosis at this point may
require using known good parts.
For a video demonstration, scan the QR code below, or
right click it and select “open in new tab”.
TESTING FOR INTERMITTENT CONDITIONS
Intermittent conditions are very difficult to diagnose, as
when you are testing the circuit, you may not have the
circuit failing to indicate where the issue is. Intermittent
electrical failures are almost always related to a poor
connection that only goes open in specific situations,
such as going over a certain kind of bump, at a certain
temperature, or when the machine is torque loaded in
one way.
Here is a list of possible failures that can be associated
with an intermittent electrical failure:
• Loose female terminal in an electrical connector.
NOTE
If the terminals in question are the correct size/series,
always use PV–43526 to test the drag when inserting
and removing the test terminal adapters. Compare the
effort to the drag against the known good tester
terminal for reference.
• Poor terminal to wire crimp.
• Terminal crimp that occurred at least partially on
insulation instead of the conductor wire strands.
• Terminal fretting corrosion
• Contamination/moisture corrosion
• A full or partial break of the conductor wires in the
insulation, with or without visible insulation damage.
• Improper routing, especially when it leads to chaffing
or heat damage, especially near exhaust.
You may need to use different techniques to duplicate
these concerns. These include but are not limited to:
• Moving the harness by wiggling it or flexing certain
areas.
• Pulling at or near the suspected connector.
• Pushing in different directions to flex the connector
body and try to isolate poor connections.
• Changing the temperature. This can be accomplished
with either heat guns or cold air guns.
WARNING
Always exercise caution when using these tools, and
use them for short periods of time when changing the
temp of an area. Failure to do so can lead to Serious
injury and/or damage to the machine.