9
CX-692
Lens kick mode jumping
The lens kick mode jumping is being executed by the
lens kick command being issued by the
microcomputer(IC501:PD5511A).The jumping direction
and the number of jumping tracks (1 - 255) are being
designated by the command. Receiving the lens kick
command, the LSI applies the kick pulse to the front
stage of the tracking EQ to execute the jumping. At
this time, the LSI works to control the moving speed of
the lens referring to the table carrying inside the LSI.
By this function, when the number of remaining tracks
is still large, the speed is raised, while the speed is
lowered as the number of remaining tracks decreases
to facilitate taking-in action by the servo when the jump
has been finished. While jumping is in progress, the
track counting is being made in observation of the RFRP
signals. Also, the jumping direction is being detected
by the phases of the RFRP and the TEZ1.
Meanwhile, when a track jumping has been finished, in
order to stabilize the taking-in action by the servo, the
tracking servo gain will be raised for about 2 to 3mS
after a jump has been finished, or with some jumps,
hysteresis movements are being employed.
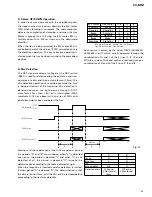
8 track jumping
Equalizer
Hysteresis
TE
RFZC
(IC401's internal signals
being formed by the RFRP)
TEZC
(IC401's internal signals
being formed by the TEI)
GAIN UP
NORMAL
ON
OFF
2-3mS
The hysteresis ON for 2mS to 3mS
for 100 or 255 track jumping only
Fig. 10