13 - PVD3627-August 2011
3.1.3.
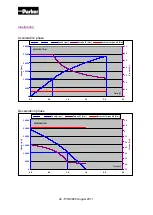
The selection of the right motor can be made through the calculation of the rms
torque
M
rms
(i.e. root mean squared torque) (sometimes called equivalent torque).
Thermal equivalent torque (rms torque)
This calculation does not take into account the thermal time constant. It can be used
only if the overload time is much shorter than the copper thermal time constant.
The rms torque
M
rms
reflects the heating of the motor during its duty cycle.
Let us consider:
- the period of the cycle
T [s],
- the successively samples of movements
i
characterized each ones by the maximal
torque
M
i
[Nm]
reached during the duration
∆
t
i
[s]
.
So, the rms torque
M
rms
can be calculated through the following basic formula:
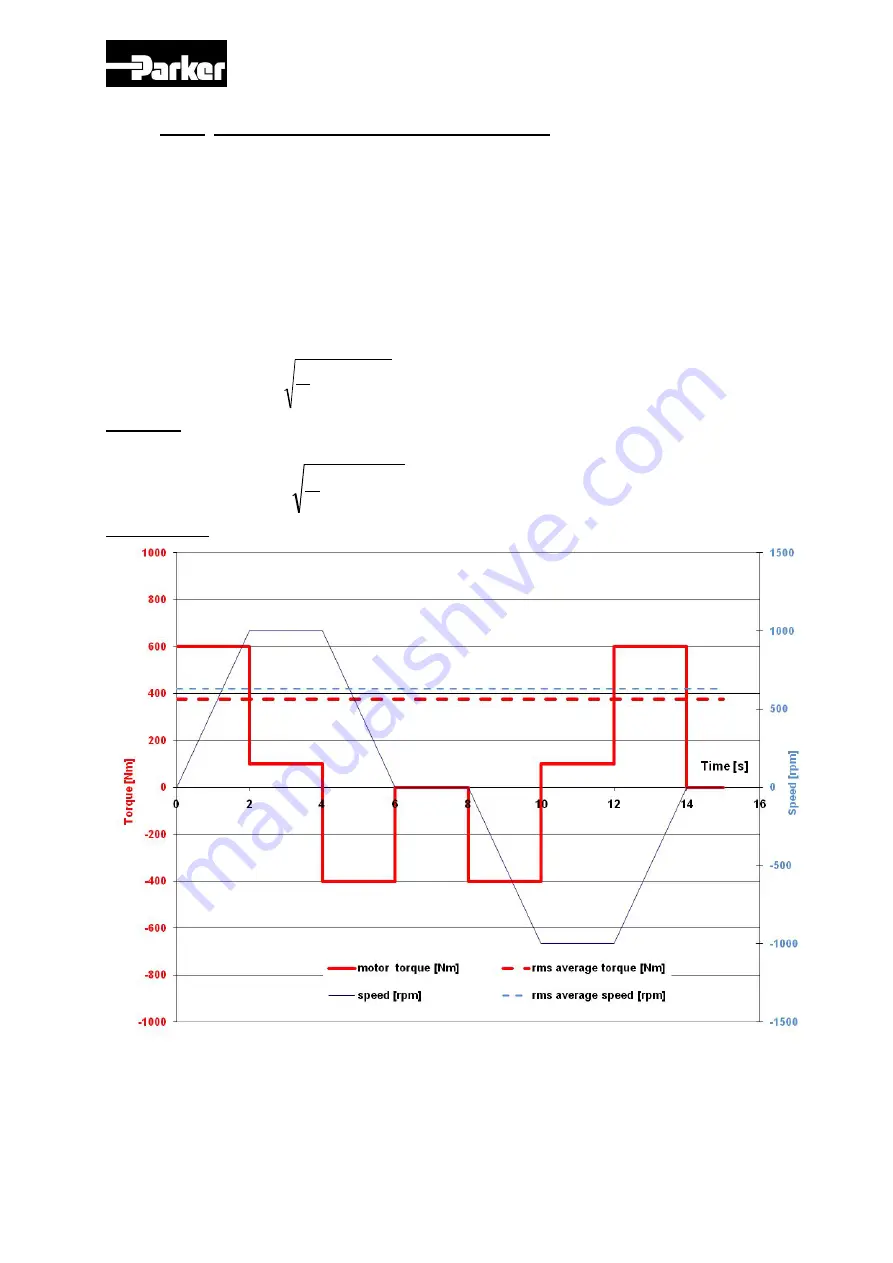
For a cycle of 2s at 0 Nm and 2s at 100Nm, the rms torque is
Example:
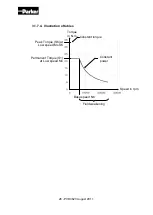
Illustration :
The maximal torque
M
i
delivered by the motor at each segment
i
of movement is
obtained by the algebric sum of the acceleration-deceleration torque and the
resistant torque.
Therefore,
M
max
corresponds to the maximal value of
M
i
.
∑
=
∆
=
n
i
i
i
rms
t
M
T
M
1
2
*
1
Nm
M
rms
7
,
70
2
*
100
*
4
1
2
=
=