IG-267-EN versión 01; 07/04/2017
26
Protection functions
General Instructions
ekor
.rpa
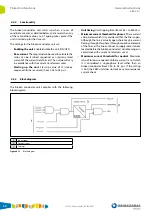
4.4.1. Estimated thermal capacity
The system estimates thermal capacity through the phase
currents (I
A
, I
B
and I
C
), using the following formula:
Where:
T
n
: Estimated thermal capacity at instant n
T
n-1
: Estimated thermal capacity at instant n-1
Δ
t: Time interval between consecutive n and n-1 instants
τ
: Cooling or heating constant If T
final
< T
n-1
, the temperature rise
constant will be applied in the formula If, on the other hand,
T
final
< T
n-1
, the cooling constant will be applied in the formula
T
final
: Final thermal capacity This value is calculated based on the
adjusted rated current and the phase currents, in accordance
with the following formula:
I
therm
: The estimated mean thermal current based on the phase
currents:
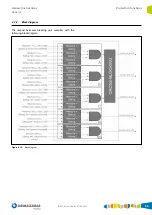
Example
The evolution of the thermal capacity estimated by the
system
for a 250 kVA transformer in a 30 kV network
under the following conditions:
I
therm
sequence read by the equipment:
Interval 1
Interval 2
Interval 3
From 0 min
to 100 min
From 100 min
to 150 min
From 150 min
to 250 min
5.8 A
1.5 A
5.8 A
Table 4.1.
I
therm
read by the system
Estimated thermal
capacity (T)
Time (min)
Figure 4.6.
Estimated thermal capacity
Starting from an initial thermal capacity of 0 %, during the
first 100 min where current is 16 % higher than the rated
(5.8 A), estimated thermal capacity reaches a value of
84.6 %.
In the next 50 min current drops to 30 % of rated current
(1.5 A), and this makes thermal capacity drop to 58.4 %.
A third interval identical to interval 1 has been chosen to
check the memory effect of the estimated thermal capacity.
In other words, a current which is 16 % higher than the rated
(5.8 A) for 100 min. It is observed that, after these 100 min,
thermal capacity reaches 106.3 %, thus exceeding 100 %
(typical trip level setting).
This difference in the estimated thermal capacity between
intervals 1 and 3 is due to the fact that previous statuses
are taken into account in the calculation. Hence, as the first
interval starts from a thermal capacity equal to 0 %, the third
interval starts from the thermal capacity accumulated up
to this moment, taking into account all the thermal stress
suffered by the element to be protected. This means the
estimated thermal capacities are different in these intervals.
Summary of Contents for ekor.rpa Series
Page 115: ......