NOVA electronics Inc. MCX514 -
176
-
176
-
(HLMT−) bit of RR2 register will become 1. When it becomes active level, driving stops.
D12 HLM-M
The bit for controlling stop type when nLMTP, nLMTM limit input signals are active.
0: instant stop, 1: decelerating stop
When limit signal is used as the stop signal of an automatic home search, set to 1: decelerating stop.
D13 SLM-E
Setting enable / disable of software limit function.
0: disable, 1: enable
Once it is enabled, if + direction software limit error occurs during the + direction driving, D0 (SLMT+) bit
of RR2 register will become 1 and if − direction software limit error occurs during the − direction driving,
D1 (SLMT−) bit of RR2 register will become 1.
・
If + direction software limit: comparative position counter
≧
SLMT+ value, then error and driving stops.
・
If − direction software limit: comparative position counter
<
SLMT− value, then error and driving stops.
Driving commands for the direction in which software limit error occurs will not be executed.
D14 SLM-O
Setting the object of software limit to real position counter or logical position counter.
0: logical position counter, 1: real position counter
D15 SLM-M
The bit for controlling stop type when software limit function is enabled.
0: decelerating stop, 1: instant stop
(Note that the bit 0/1 is opposite of the bit for controlling stop type of hardware limit signals.)
D15~D0 will be set to 0 at reset.
6.7
Mode Register3: WR3
Each axis has mode register WR3 individually. The host CPU specifies the mode register of which axis should be accessed
depends on the axis of written command just before. Or the user can specify the axis by writing NOP command with axis
assignment.
Mode register WR3 is used for setting: (1). manual deceleration, (2). acceleration/deceleration mode (symmetry / non-symmetry,
linear acceleration/deceleration, S-curve acceleration/deceleration), (3). drive pulse output mode, (4). encoder input mode,
(5). limit signal pin inversion, (6). trapezoid triangle form prevention function, (7). repeat timer.
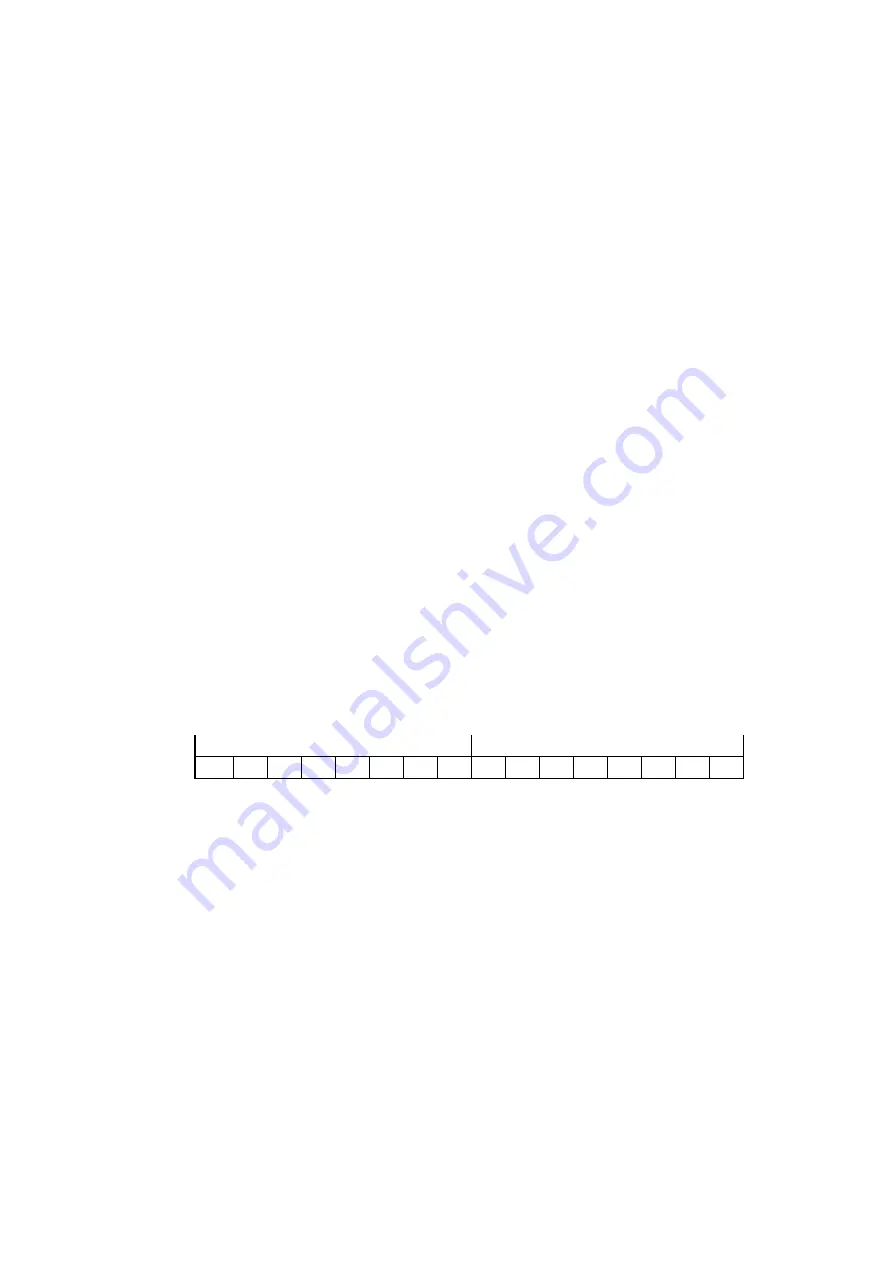
D7
D6
D5
D4
H
L
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
D3
D2
D1
D0
WR3
MANLD
DSNDE
SACC
DPMD0
DPMD1
DP-L
DIR-L
DPINV
PIMD0
PIMD1
PI-L
PIINV
LMINV
AVTRI
TMMD
0
D0 MANLD
Setting manual / automatic deceleration for fixed pulse acceleration / deceleration driving.
0: automatic deceleration, 1: manual deceleration
The decelerating point (DP) should be set if the manual deceleration mode is engaged.
D1 DSNDE
Setting decelerating rate whether to use the rate of the acceleration (symmetry) or an individual decelerating
rate (non-symmetry).
Set whether jerk (symmetry) or an individual deceleration increasing rate (non-symmetry) is used as a
deceleration increasing rate at S-curve deceleration.
0: symmetry acceleration/deceleration, 1: non-symmetry acceleration/deceleration
Automatic deceleration cannot be performed for non-symmetrical S-curve acceleration / deceleration fixed
pulse driving. In this case, the D0 (MANLD) bit must be set to 1 and a manual deceleration point (DP) must
be set.
D2 SACC
Setting the speed curve to either linear driving or S-curve driving during acceleration/deceleration driving.
0: linear driving, 1: S-curve driving
Before S-curve driving is engaged, jerk (JK) (deceleration increasing rate (DJ)) must be set.






























