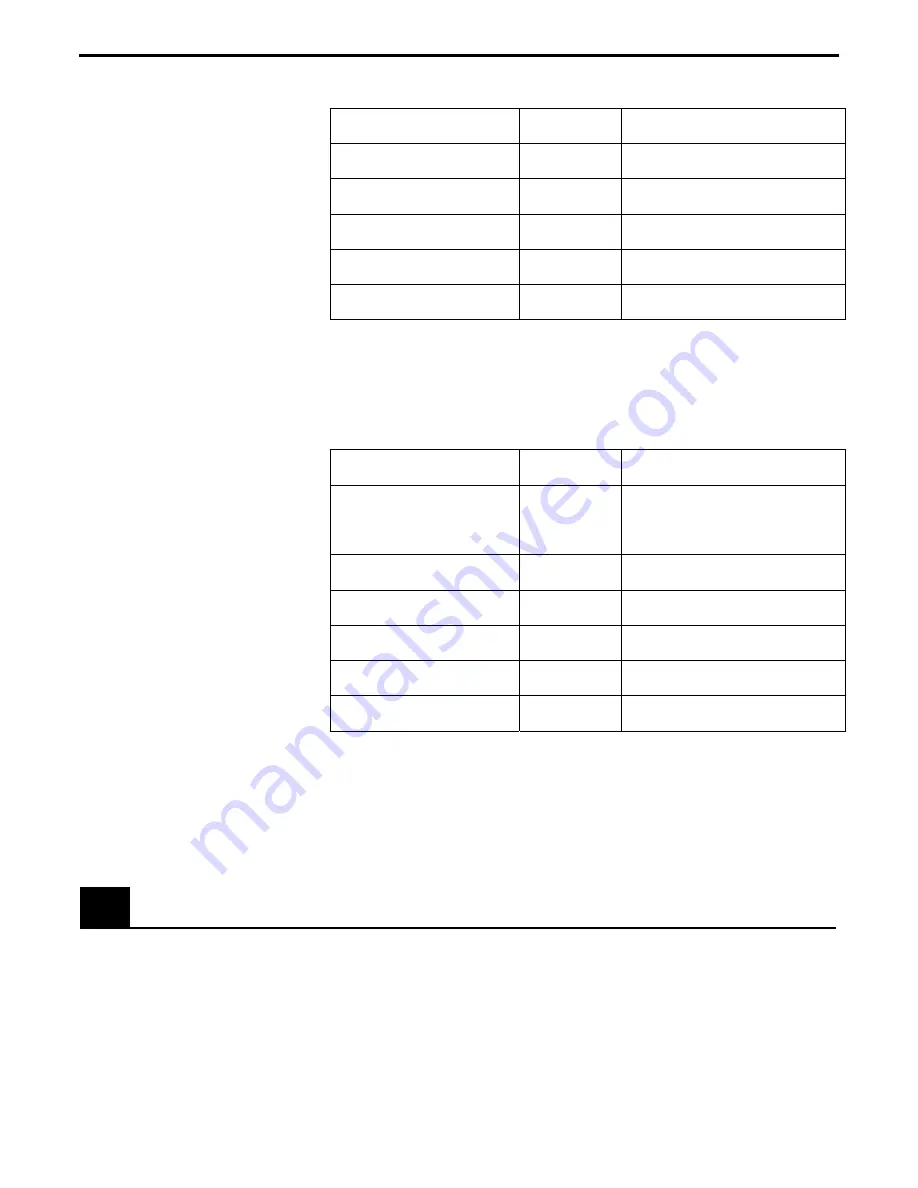
Steps Move
Command
Action by Move Command
1. Define master-slave
relationship
2SS4
Axis #2 is the slave of axis #4
2. Define slave axis jog.
Velocity update interval
2S1100
Update slave axis jog velocity
every 100 milliseconds
3. Define slave axis scaling
coefficients
2SK0.5, 0
Specify scaling coefficients
4. Define slave axis
trajectory mode
2TJ6
Set slave axis trajectory mode
5. Move the master axis
physically
Table 4.2: Slave to a Trackball Steps
4.2.4 Slave to a Joystick
If the slave axis is required to jog based on a DIO bit status (such as
through joystick), follow these steps:
Steps Move
Command
Action by Move Command
1. Assign DIO bits for
jogging slave axis
2BP0, 1
Jog axis #2 in negative direction if
DIO bit #0 is low. Jog axis #2 in
positive direction if DIO bit #1 is
low.
2. Enable DIO bits for jog
mode
2BQ1
3. Define slave axis jog
velocity update interval
2SI100
Update slave axis jog velocity
every 100 milliseconds
4. Define slave axis scaling
coefficients
2SK0.5, 0
Specify scaling coefficients
5. Define slave axis
trajectory mode
2TJ6
Set slave axis trajectory mode
6. Change DIO bit value
physically
Table 4.3: Slave to a Joystick Steps
Refer to the description of the ASCII commands in Section 3: Remote
Mode, for additional description, correct syntax, parameter ranges,
etc.
4.3
Closed Loop Stepper Motor Positioning
4.3.1 Introduction – Closed Loop Stepper
Most of the electro-mechanical systems are subjected to phenomena
such as backlash and friction.
Section 4 – Advanced Capabilities
4-9
Summary of Contents for ESP300 Series
Page 1: ...ESP300 Motion Controller Driver User s Manual...
Page 4: ...ESP300 1999 EU Declaration of Conformity iv Preface...
Page 29: ...This page is intentionally left blank Section 2 Modes of Operation 1 15...
Page 30: ......
Page 230: ...4 16 Section 4 Advanced Capabilities...
Page 274: ...This page is intentionally left blank 6 6 Section 6 Servo Tuning...
Page 290: ...This page is intentionally left blank B 6 Appendix B Trouble Shooting and Maintenance...
















































