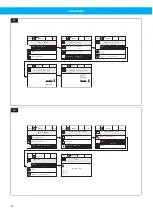
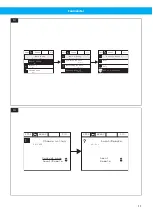
Fan Inverter
2.3 ATEX
WARNING! Explosion risk
An EX motor with a converter supply must be selected for such an application.
According to EN 60079-14, for EX d, EX n and EX tD motors, there shall be a device for a direct temperature con-
trol by embedded temperature sensors specified in the motor manufacturer’s documentation for limiting the
surface temperature of the motor housing. The device electrically disconnects the motor if the housing be-
comes overheated.
If the STO and ATEX optional board is installed, see the VACON 100 OPTBJ STO and ATEX Option Board Safety
Manual (C) in
. Contact Nederman for more information.
3 Description
3.1 Intended use
Nederman Fan Inverter is a frequency controller that is preprogrammed with an extraction fan application for
Nederman fans. It is equipped with a pressure sensor and a PID controller that can maintain a constant negative
pressure in an extraction system, and as a result, maintain an almost constant airflow in extraction devices. The
fan capacity is regulated to the actual demand of the airflow, depending on the number of extraction devices in
use at the same time.
The benefit of using Nederman Fan Inverter is that it reduces running costs, heat loss to the atmosphere and
noise levels. It conserves energy and improves performance by regulating the system’s power usage as the de-
mand from extraction devices increases or decreases.
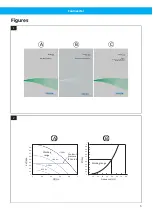
4 Frequency controlled fan
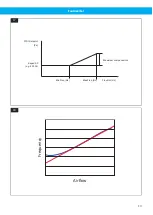
When a fan is frequency controlled by Nederman Fan Inverter, a constant pressure can be achieved within the
entire working range of the fan, up to the fan maximum frequency. See
(A).
For example, if the fan frequency is reduced by half, the power is reduced to 1/8. As the power consumption in-
creases dramatically with the frequency, using any frequency higher than the nominal frequency will overload
the motor. See
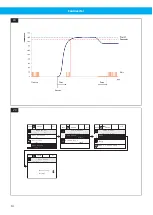
However, although the cooling effect from the motor cooling fan is reduced when the frequency is decreased,
the power consumption is reduced even more, so there is normally no risk of overheating the fan motor by redu-
cing the frequency.
WARNING! Risk of personal injury
For Nederman fans, the maximum frequency is the fan nominal frequency, which is normally either 50 or
60 Hz. Do not exceed the fan’s nominal frequency since it imposes too much mechanical stress on the im-
peller.
17