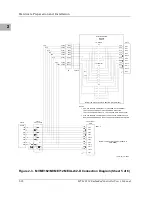
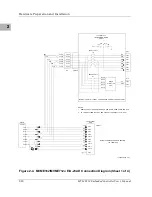
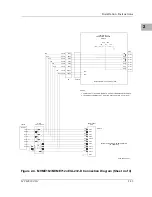
Memory Maps
MVME162/D2
3-3
3
Memory Maps
There are two points of view for memory maps:
❏
The mapping of all resources as viewed by local bus masters (local bus
memory map)
❏
The mapping of onboard resources as viewed by VMEbus masters
(VMEbus memory map)
Local Bus Memory Map
The local bus memory map is split into different address spaces by the
Transfer Type (TT) signals. The local resources respond to the normal access
and interrupt acknowledge codes.
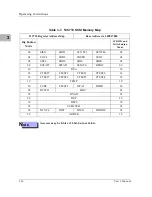
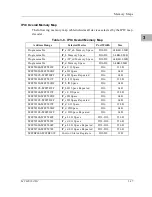
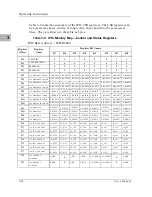
Normal Address Range
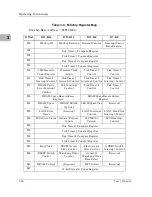
The memory map of devices that respond to the normal address range is
shown in the following tables. The normal address range is defined by the TT
signals on the local bus. For the MVME162, transfer types 0, 1, and 2 define the
normal address range. Table 3-1 defines the entire map ($00000000 to
$FFFFFFFF). Many areas of the map are user-programmable, and suggested
uses are shown in the table. The cache inhibit function is programmable in the
MC68xx040 MMU. The onboard I/O space must be marked ‘‘cache inhibit’’
and serialized in its page table. Table 3-2 further defines the map for the local
I/O devices.
Summary of Contents for MVME162
Page 1: ...MVME162 Embedded Controller User s Manual MVME162 D2 ...
Page 6: ......
Page 10: ...x ...
Page 12: ...xii ...
Page 14: ...xiv ...
Page 52: ...Hardware Preparation and Installation 2 26 MVME162 Embedded Controller User s Manual 2 ...
Page 64: ...Operating Instructions 3 12 User s Manual 3 This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 78: ...Operating Instructions 3 26 User s Manual 3 ...
Page 92: ...Functional Description 4 14 User s Manual 4 Figure 4 1 MVME162 Main Module Block Diagram ...