5-18
MPC8240 Integrated Processor User’s Manual
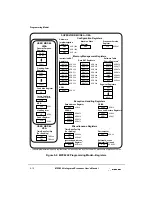
Programming Model
5.3.2 PowerPC Instruction Set and Addressing Modes
All PowerPC instructions are encoded as single-word (32-bit) opcodes. Instruction formats
are consistent among all instruction types, permitting efficient decoding to occur in parallel
with operand accesses. This fixed instruction length and consistent format greatly simplifies
instruction pipelining.
5.3.2.1 Calculating Effective Addresses
The effective address (EA) is the 32-bit address computed by the processor when executing
a memory access or branch instruction or when fetching the next sequential instruction.
The PowerPC architecture supports two simple memory addressing modes:
•
EA = (rA|0) + offset (including offset = 0) (register indirect with immediate index)
•
EA = (rA|0) +7 rB (register indirect with index)
These simple addressing modes allow efficient address generation for memory accesses.
Calculation of the effective address for aligned transfers occurs in a single clock cycle.
For a memory access instruction, if the sum of the effective address and the operand length
exceeds the maximum effective address, the memory operand is considered to wrap around
from the maximum effective address to effective address 0.
Effective address computations for both data and instruction accesses use 32-bit unsigned
binary arithmetic. A carry from bit 0 is ignored in 32-bit implementations.
In addition to the functionality of the MPC603e, the MPC8240 has additional hardware
support for misaligned little-endian accesses. Except for string/multiple load and store
instructions, little-endian load/store accesses not on a word boundary generate exceptions
under the same circumstances as big-endian requests.
5.3.2.2 PowerPC Instruction Set
The PowerPC instructions are divided into the following categories:
•
Integer instructions—These include computational and logical instructions.
— Integer arithmetic — divide instructions execute with a shorter latency as
described in Section 5.7, “Instruction Timing.”
— Integer compare
— Integer logical
— Integer rotate and shift
•
Floating-point instructions—These include floating-point computational
instructions, as well as instructions that affect the FPSCR.
— Floating-point arithmetic
— Floating-point multiply/add
— Floating-point rounding and conversion
Summary of Contents for MPC8240
Page 1: ...MPC8240UM D Rev 1 1 2001 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual ...
Page 38: ...xviii MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual TABLES Table Number Title Page Number ...
Page 48: ...xlviii MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual Acronyms and Abbreviations ...
Page 312: ...6 94 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual ROM Flash Interface Operation ...
Page 348: ...7 36 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual PCI Host and Agent Modes ...
Page 372: ...8 24 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual DMA Register Descriptions ...
Page 394: ...9 22 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual I2O Interface ...
Page 412: ...10 18 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual Programming Guidelines ...
Page 454: ...12 14 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual Internal Arbitration ...
Page 466: ...13 12 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual Exception Latencies ...
Page 516: ...16 14 Watchpoint Trigger Applications ...
Page 538: ...B 16 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual Setting the Endian Mode of Operation ...
Page 546: ...C 8 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual ...
Page 640: ...INDEX Index 16 MPC8240 Integrated Processor User s Manual ...