8.5 Homing
Homing serves to establish an absolute position reference (referred to the entire
axis), and must usually be performed once after power-up. Homing is necessary
when absolute positioning operations are carried out without absolute encoders
(e.g. SSI multi-turn encoders). For all other positioning operations (relative, infinite)
no homing is required. For zero position adjustment of absolute encoders homing
method -5 is available. There are various methods, which can be set according to
the application.
The selection of a homing method defines:
The reference signal (positive limit switch, negative limit switch, reference
cam)
The direction of the drive
The position of the zero pulse
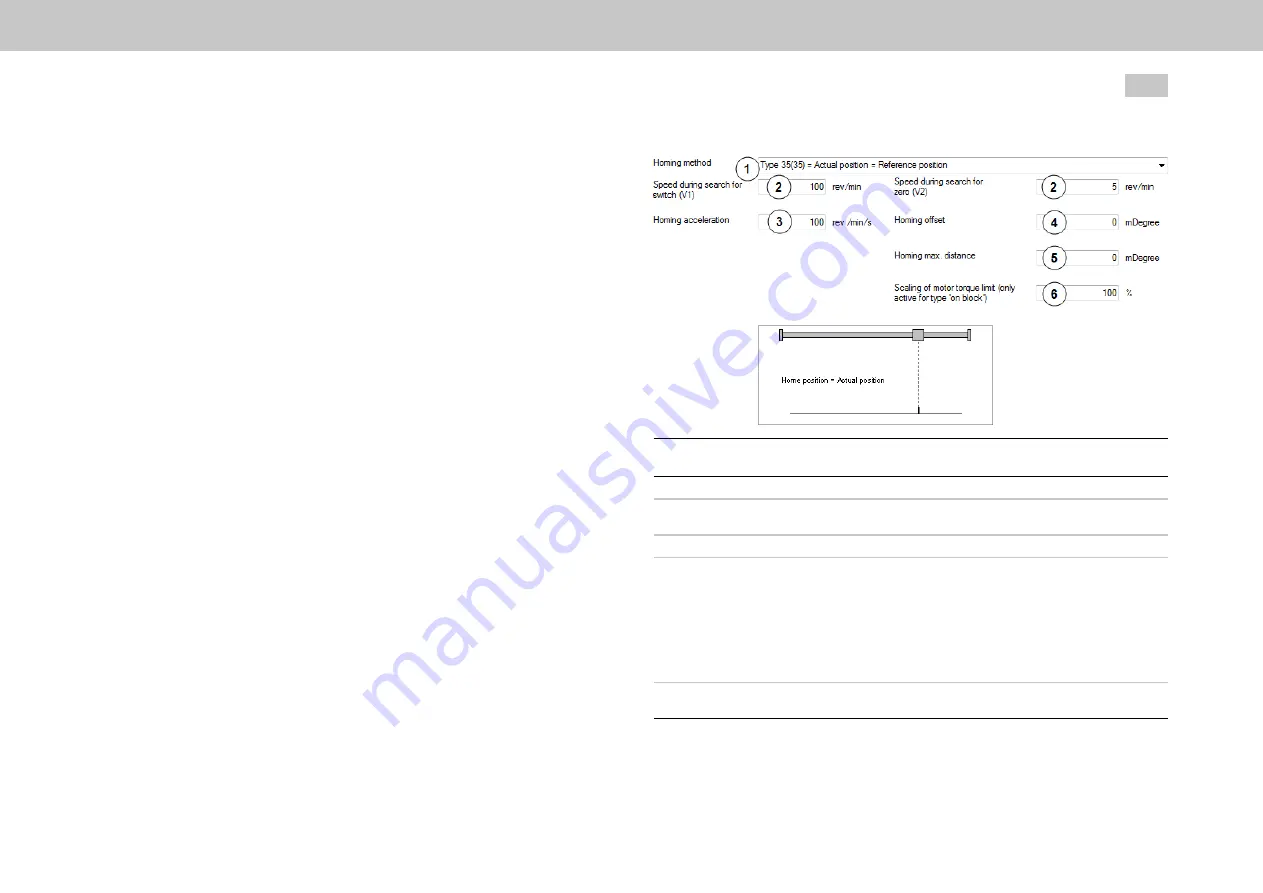
8.5.1 Homing dialog box
The homing movement is dictated by the speed (velocity) V1 and V2, the
acceleration and the maximum positioning range.
MOOG
ID
No.:
CB40859-001
Date:
02/2018
MSD Servo Drive - Device Help
189
8 Motion profile
Fig. 8.38:
Selection
method selection
①
Selection of homing methods (-12) to (35)
②
Speed V1: Speed during cam search
Speed V2: Speed during zero point search
③
Acceleration for V1 and V2
④
The reference point usually has an actual position value defined on the axis side
referred to the axis zero.
Ideally, the position value of the drive-side datum point and of the reference point
would be identical.
As the position of the datum point is decisively influenced by
the encoder mounting, however, the datum and reference points differ.
To establish a positional reference to the real axis zero, the desired axis-related
actual position value of the reference point should be set via the zero offset.
⑤
Limitation of positioning range for homing. On exiting the positioning range, the
axis is stopped with the error message "Overrun".
Legend to “‘Homing method’ screen” figure






























