10. Safety system
MiR1000 Shelf Lift User Guide (en) 12/2020 - v.2.1 ©Copyright 2019-2020: Mobile Industrial Robots A/S.
103
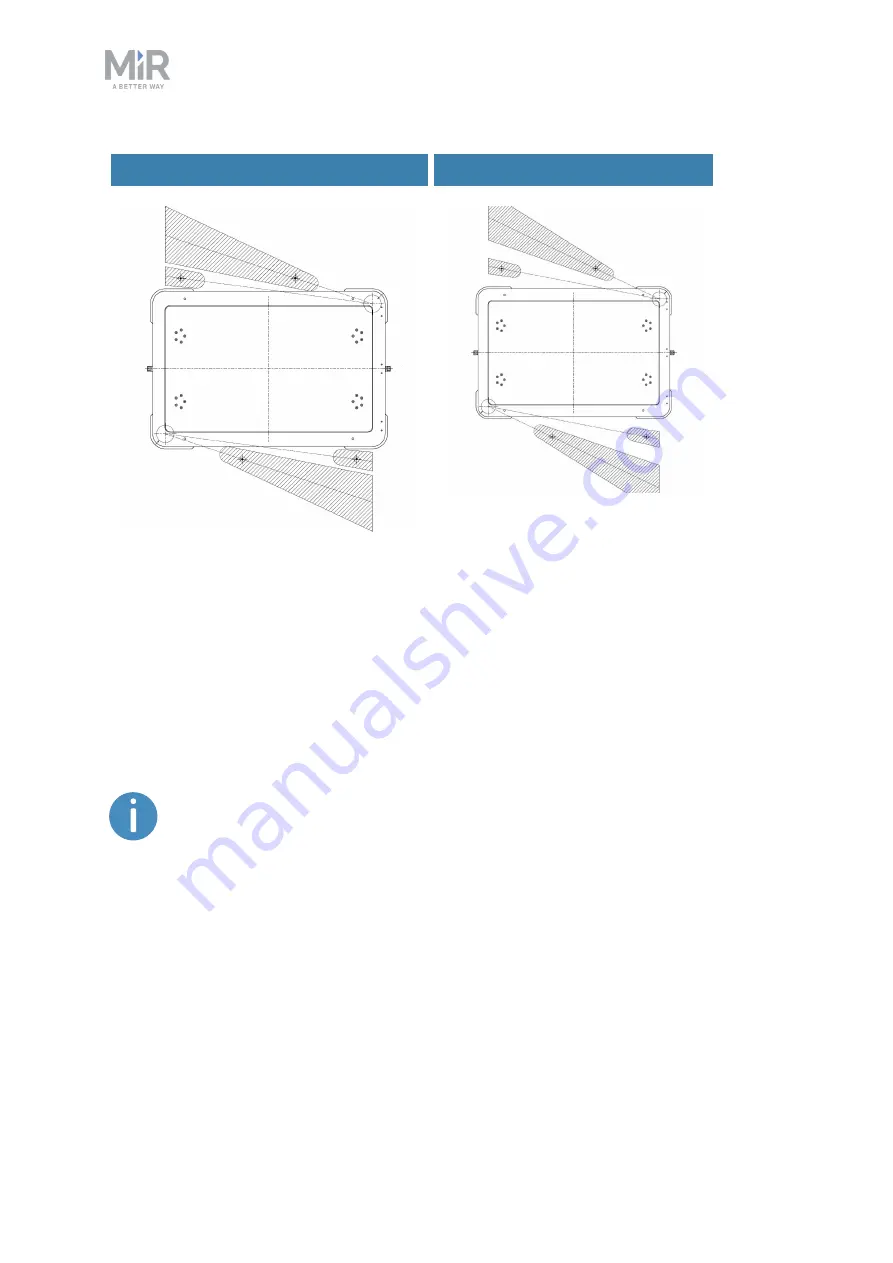
Narrow asymmetric shelf
Wide asymmetric shelf
Figure 10.10. The illustrations shows the blind spots around the shelf legs in the Protective fields when the
robot is carrying an asymmetric shelf. The blind spots are smallest when using asymmetric shelves.
By default, the shelf specific Protective field sets are designed for asymmetric shelves with
dimensions supported by MiR—see
Shelf specifications on page 112
. This design minimizes
the blind spots at the most critical areas. If you are using shelves that are not supported by
MiR's design guidelines, the Protective field sets must be changed and the safety system
recertified—see
Adjusting the Protective field sets on page 117
.
Shelves with symmetric legs create significantly larger blind spots for the
robot than shelves with asymmetric legs because the legs interfere more with
the field of view of the laser scanners.
The lift uses input pins 11 and 12 in the Auxiliary safety functions interface to signal whether
the lift is raised or lowered—see
Interface specifications on page 225
. These two input pins
are connected to the 24 V output in pins 1 and 2 through the mechanical switches in the lift.
When the lift is lowered, the switches are pressed down and closes the circuit so 24 V is
delivered to pins 11 and 12. When the lift is raised, the input pins receive 0 V.
















































