MP 26/10
Installation and Calibration Manual
Minebea Intec
EN-25
4.4.
Example: Calibration by Value
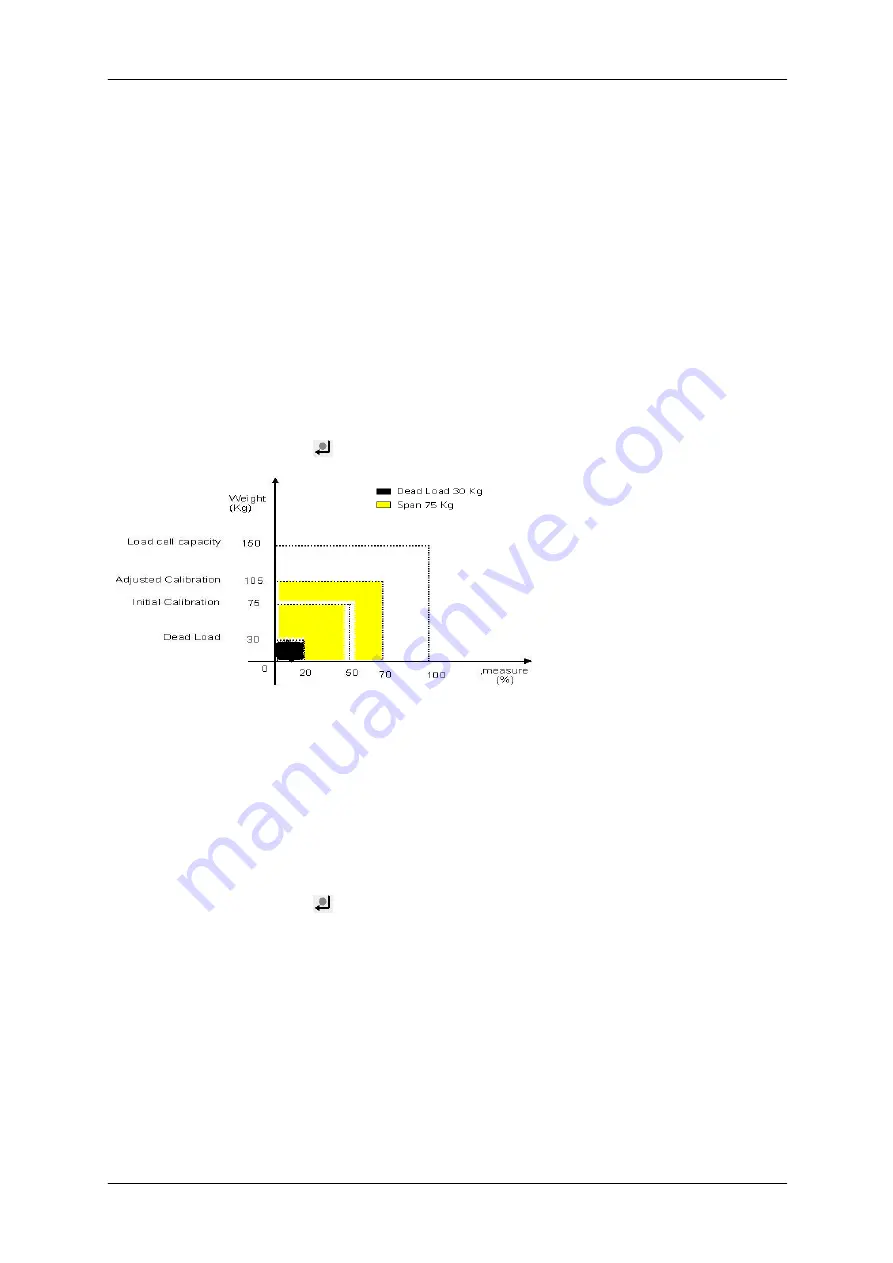
For example, consider a load cell with 150 kg capacity and a sensitivity of 2mV/V. The voltage between V+ and
V- is 10 V. We want to calibrate the system for the 75-kg full-scale capacity plus an unknown dead load.
Assumption:
No load produces 0 mV which is 0%, so enter InL.1 =0 (entry = %), OuL.1 =0 (display = kg)
A full load produces 20 mV 10 V, i.e. 150 kg corresponds to 20 mV which is 100%.
output signal =
power supply *
sensitivity of load cell
(@ max. capacity)
20 mV =
10 V *
2 mV/V
(@ 150 kg)
100 %
Solution:
We want the system to be calibrated for 75 kg.
The first step is to determine the Pspan [%] assuming no dead load is present in the system:
Set InL.1 =0, OuL.1 =0.
Pspan [%] = (full scale * 100) / (total capacity of load cell).
Pspan [%] = (75 *100) /150 produces Pspan = 50
Enter InH.1 = 50 (entry = %) and OuH.1 = 75 (display = kg)
Save the data to the device (Press
to move to end).
Now, the device shows the dead load as a weight value as xxxx kg.
If the device shows 30 kg, dead load = xxxx = 30.
The second step is to adjust the dead load and calibration point
Pdead [%] = (dead load * 100) / (max. capacity of load cell).
Pdead [%] = (30 * 100)/150 = 20
Set InL.1 =Pdead =20 (entry = %);
OuL.1 =dead Load= 0 (display = kg);
InH.1 = 50+Pdead = 70 (entry = %);
OuH.1 = 75 (display = kg)
Save the data to the device (Press
to move to end).
Now the device has adjusted its dead load and the display shows Zero.


























