© Microhard Systems Inc.
180
Appendix C: Port Forwarding Example (Page 1 of 2)
By completing the Quick Start process, a user should have been able to log in and set up the IPn4G to
work with their cellular carrier. By completing this, the modem is ready to be used to access the internet
and provide mobile connectivity. However, one of the main applications of the IPn4G is to access
connected devices remotely. In order to do this, the IPn4G must be told how to deal with incoming traffic,
where to send it to. To accomplish this there are three options :
- IP-Passthrough
- Port Forwarding
- DMZ (a type of Port Forwarding)
In the previous section we illustrated how to use and setup IP-Passthrough. In this section we will talk
about port forwarding. Port forwarding is ideal when there are multiple devices connected to the IPn4G, or
if other features of the IPn4G are required (Serial Ports, Firewall, GPS, etc). In port forwarding, the IPn4G
looks at each incoming Ethernet packet on the WAN and by using the destination port number, determines
where it will send the data on the private LAN . The IPn4G does this with each and every incoming packet.
DMZ (a form of port forwarding) is useful for situations where there are multiple devices connected to the
IPn4G, but all incoming traffic is destined for a single device. It is also popular to use DMZ in cases where
a single device is connected but several ports are forwarded and other features of the IPn4G are required,
since in passthrough mode all of these features are lost.
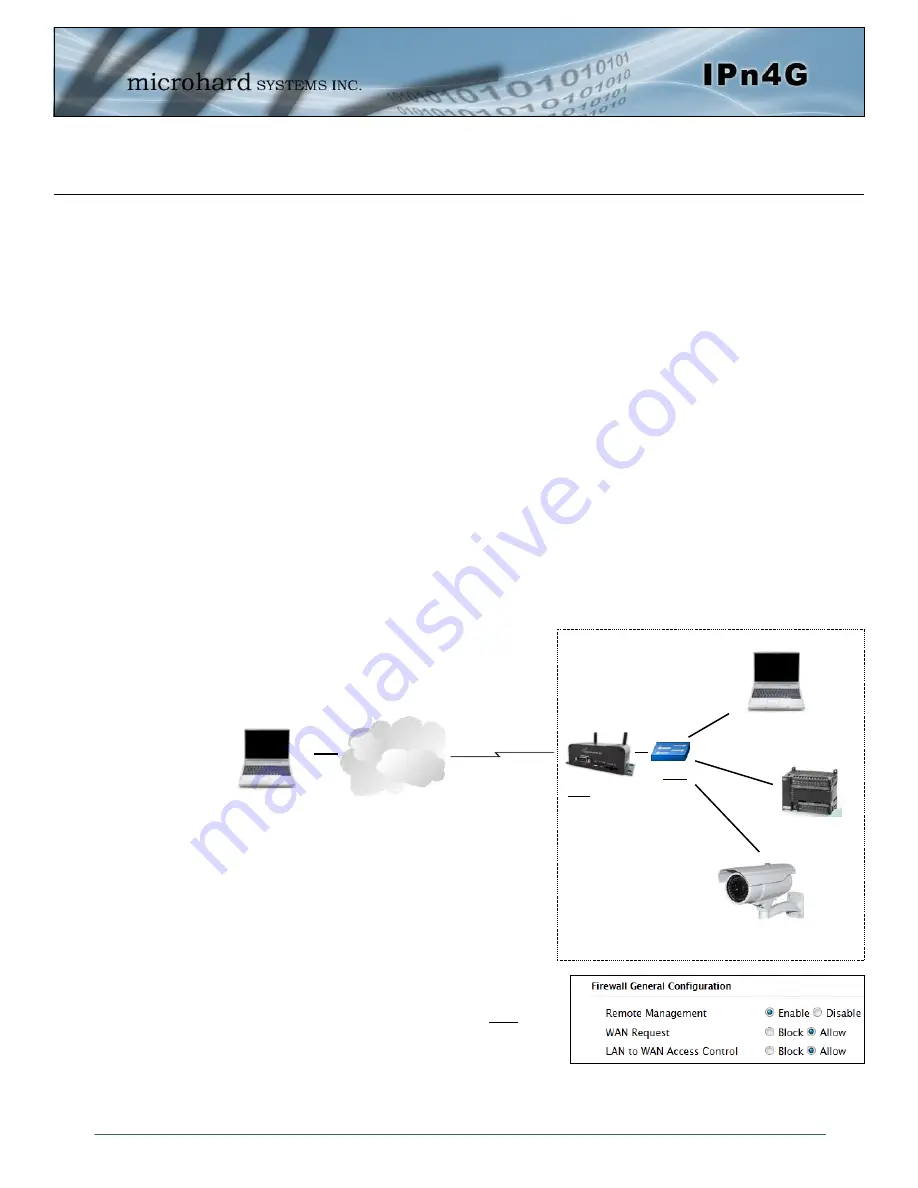
Consider the following example. A user has a remote location that has several devices that need to be
accessed remotely. The User at PC1 can only see the IPn4G directly using the public static IP assigned by
the wireless carrier, but not the devices behind it. In this case the IPn4G is acting a gateway between the
Cellular Network and the Local Area Network of its connected devices. Using port forwarding we can map
the way that data passes through the IPn4G.
Step 1
Log into the IPn4G (Refer to Quick Start), and ensure that the
Firewall
is enabled. This can be found under
Firewall >
General.
Also ensure that
WAN Request
is set to Allow, which
allows traffic to come in from the WAN/4G, or that sufficient
Rules
or
IP lists
have been setup to allow specific traffic to pass
through the IPn4G. Once that is complete, remember to “Submit”
the changes.
Cellular Network/
Internet
IPn4G
WAN IP:
74.198.186.193
(Cellular Carrier)
LAN IP:
192.168.168.1
PC2: 192.168.168.20
Webserver on port 80
Wireless Cellular
Connection
PC1: Connected to
internet.
PLC/RTU: 192.168.168.30
Webserver on port 80
Modbus on port 502
IP Camera: 192.168.168.40
Webserver on Port 80
Wired or Wireless
Devices
Switch














































