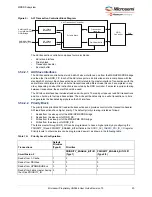
MDDR Subsystem
Microsemi Proprietary UG0446 User Guide Revision 7.0
26
Supported burst modes for DDR SDRAM types and PHY widths are listed in the following table. For
M2GL050 devices, only sequential burst mode and a burst length of 8 are supported.
Note:
The burst length 16 is supported for LPDDR1 if bus width is 16 except M2GL050.
3.5.5.4
Configuring Dynamic DRAM Constraints
Timing parameters for DDR memories must be configured according to the DDR memory specification.
Dynamic DRAM constraints are subdivided into three basic categories:
•
Bank constraints affect the transactions that are scheduled to a given bank.
•
Rank constraints affect the transactions that are scheduled to a given rank.
•
Global constraints affect all transactions.
3.5.5.5
Dynamic DRAM Bank Constraints
The timing constraints which affect the transactions to a bank are listed in the following table. The control
bit field must be configured as per the DDR memory vendor specification.
Table 13 •
Supported Burst Modes
Bus Width
Memory Type
Sequential/Interleaving
4
8
32
LPDDR1
✓
✓
DDR2
✓
✓
DDR3
–
✓
16
LPDDR1
–
✓
DDR2
–
✓
DDR3
–
✓
8
LPDDR1
–
✓
DDR3
–
✓
DDR2
–
Table 14 •
Dynamically Enforced Bank Constraints
Timing Constraint of DDR
Memory
Control Bit
Description
Row cycle time (t
RC
)
Minimum time between two successive activates to
a given bank.
Row precharge command
period (t
RP
)
Minimum time from a precharge command to the
next command affecting that bank.
Minimum bank active time
(t
RAS(min)
)
Minimum time from an activate command to a
precharge command to the same bank.
Maximum bank active time
(t
RAS(max)
)
Maximum time from an activate command to a
precharge command to the same bank.
RAS-to-CAS delay (t
RCD
)
Minimum time from an activate command to a
Read or Write command to the same bank.
Write command period (t
WR
)
Minimum time from a Write command to a
precharge command to the same bank.
Read-to-precharge delay
(t
RTP
)
Minimum time from a Read command to a
precharge command to the same bank.
Set this to the current value of additive latency plus
half of the burst length.