www.procontechnology.com.au
3 Phone: (03) 98306288
Recovery Circuits
a. Automatic Recovery
Automatic Recovery senses the removal of the fault condition and returns the unit to normal operation.
b. Manual Recovery
Before proceeding with Manual Recovery, make sure that the fault condition is removed. Manual Recovery requires cycling the
input power off and on.
Overcurrent /Overload Precautions
Protection and Recovery circuits are designed to prevent damage to the device during an Overcurrent or Overload condition.
However, leaving a device overloaded (or shorted) for extensive periods of time is NOT recommended and may result in
reduced life and/or damage to the DC-DC converter.
2.3 OVER TEMPERATURE PROTECTION (OTP)
Some DC-DC converters have an excessive temperature shut down circuit. When the unit's operating temperature is too high,
the protection circuit will shut down the output. Some common causes of excessive temperature are Overcurrent/Overload, high
ambient temperature or restricted ventilation (e.g. faulty cooling fan). Automatic or manual recovery can occur once the cause
of the over temperature condition is removed (high ambient temperature and/or high load).
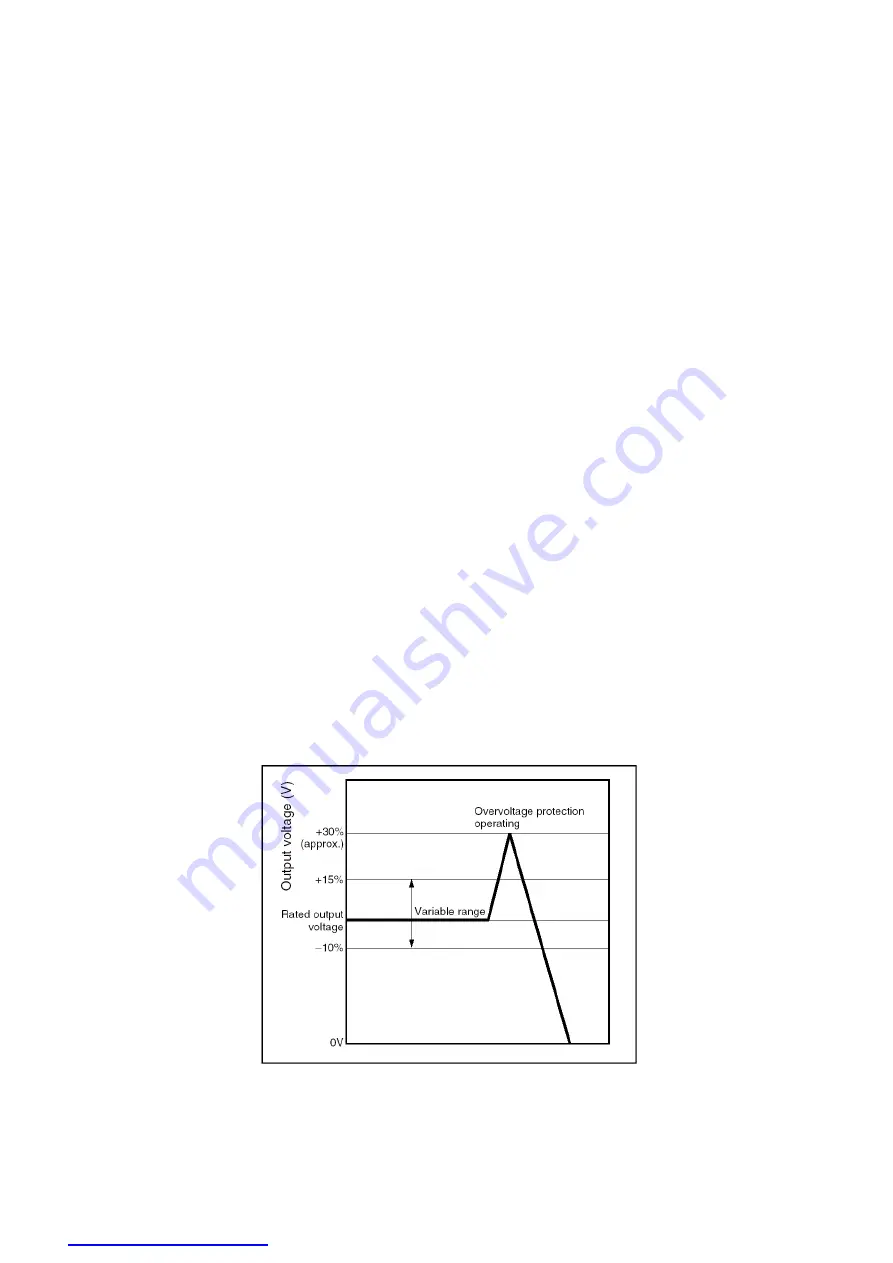
2.4 OVER VOLTAGE PROTECTION (OVP)
When the output voltage exceeds the rated value by approximately 130%, the unit will be protected by the following three
possible methods to prevent damage to the components at the load terminals:
a. Shut down the output voltage. Reset the DC-DC converter by turning it OFF for several seconds and then back ON again.
b. Hiccup mode. The output will shut down for a few seconds and then attempt to restart automatically.
Over Voltage Protection may be triggered by a fault within the converter, most commonly by setting the output voltage trim pot
too high (especially when switching inductive loads) or it can occur when an external voltage is applied to the output. Using an
external voltage applied to the output terminals, provides a simple means of testing the over voltage threshold of a DC-DC
converter. Note, excessive voltage or reverse polarity voltages applied to the output can damage a DC-DC converter!
There are three kinds of Over Voltage Protection:
a. Disabling the control circuit controlling the feedback loop shutting down the unit.
b. Shorting the output by using a "Crowbar" activating the unit's overcurrent/overload protection.
c. Clamping the output voltage by using a zener diode.
Fig. 5































