11-31
Appendix > Glossary
Send as E-mail
A function to send the image data stored in the machine as an E-mail attachment. E-mail addresses
can be selected from the list or entered at each time.
SMTP (Simple Mail
Transfer Protocol)
A protocol for E-mail transmission over the Internet or an intranet. It is used for transferring mail
between mail servers as well as for sending mail from clients to their servers.
Status Page
The page lists machine conditions, such as the memory capacity, total number of prints and scans,
and paper source settings.
Subnet Mask
The subnet mask is a way of augmenting the network address section of an IP address.
A subnet mask represents all network address sections as 1 and all host address sections as 0. The
number of bits in the prefix indicates the length of the network address. The term "prefix" refers to
something added to the beginning and, in this context, indicates the first section of the IP address.
When an IP address is written, the length of the network address is indicated by the prefix length after
a forward slash (/). For example, "24" in the address "133.210.2.0/24". In this way, "133.210.2.0/24"
denotes the IP address "133.210.2.0" with a 24-bit prefix (network section). This new network address
section (originally part of the host address) made possible by the subnet mask is referred to as the
subnet address. When you enter the subnet mask, be sure to set the "DHCP" setting to "Off".
TCP/IP (IPv6)
TCP/IP (IPv6) is based on the current Internet protocol, TCP/IP (IPv4). IPv6 is the next-generation
Internet protocol and expands the available address space, which resolves the problem of the lack of
addresses under IPv4, while also introducing other improvements such as additional security
functionality and the capacity to prioritize data transmission.
TCP/IP (Transmission
Control Protocol/
Internet Protocol)
TCP/IP is a suite of protocols designed to define the way computers and other devices communicate
with each other over a network.
TWAIN (Technology
Without An Interesting
Name)
A technical specification for connecting scanners, digital cameras, and other image equipment to
computers. The TWAIN compatible devices enable you to process image data on any relevant
application software. TWAIN is adopted on a large amount of graphic software (e.g. Adobe
Photoshop) and OCR software.
USB (Universal Serial
Bus) 2.0
A USB interface standard for Hi-Speed USB 2.0. The maximum transfer rate is 480 Mbps. This
machine is equipped with USB 2.0 for high-speed data transfer.
WIA (Windows Imaging
Acquisition)
A function to import images supported after Windows Me/XP from digital cameras and other peripheral
devices. This function replaces what TWAIN used to do. The feature is provided as a part of Windows
functions and improves ease of operation, so that you import images directly to My Computer without
using any application.
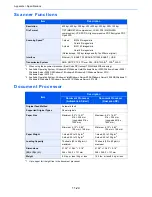
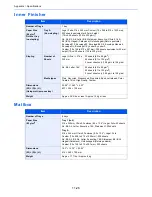
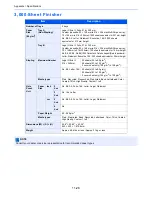
Item
Explanation
Summary of Contents for TASKalfa 356ci
Page 1: ...OPERATION GUIDE q PRINT q COPY q SCAN q FAX TASKalfa 356ci TASKalfa 406ci ...
Page 463: ...10 22 Troubleshooting Regular Maintenance 4 Install the Punch Waste Box 5 Close the cover ...
Page 504: ...10 63 Troubleshooting Clearing Paper Jams 8 Remove any jammed paper 9 Push Right Cover 1 ...
Page 564: ......